Safety and efficacy after switch to a saquinavir-containing antiretroviral regimen in protease inhibitor pretreated HIV-positive patients
- PMID: 20952345
- PMCID: PMC3351903
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-783x-15-9-369
Safety and efficacy after switch to a saquinavir-containing antiretroviral regimen in protease inhibitor pretreated HIV-positive patients
Abstract
Objective: the RAINBOW survey is a multinational observational study assessing the tolerability and efficacy of ritonavir-boosted saquinavir (SQV/r), using the 500 mg film-coated SQV formulation, in routine clinical practice. This analysis presents data from the German subgroup of protease inhibitor (PI)-pretreated, but SQV-naive patients.
Methods: multicenter, prospective, open-label, 48 week cohort study. Efficacy assessments included the proportion of patients with HIV-1 RNA <50 and <400 copies/mL and changes in CD4 cell count from baseline to week 48. Tolerability assessments included changes in liver enzymes and lipid levels from baseline to week 48.
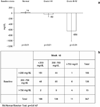
Results: a total of 426 patients were included in the analysis. The proportion of patients with HIV RNA levels <50 copies/mL at week 48 was 60.3 % (compared with 31.7% at switch to SQV/r) (intent-to-treat, last observation carried forward analysis). After 48 weeks, median CD4 count increased by +61 cells/mm3 from baseline (p<0.01) and 60.3% of patients achieved HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL. Median changes in fasting triglyceride levels (stratified according to baseline level) at week 48 were: +14 mg/dL (IQR -8; 57) for patients with baseline triglyceride <200 mg/dL; -50 mg/dL (IQR -139; 0) for baseline triglyceride 200-750 mg/dL, and -656 mg/dL (IQR -1024; 0) for baseline triglyceride >750 mg/dL (p<0.01 for all). Median changes in fasting total cholesterol (TC) levels (stratified according to baseline) were +16 mg/dL (IQR -3; 43) for patients with baseline TC <200 mg/dL (p<0.01), -3 mg/dL (IQR -25; 25) for baseline TC 200-300 mg/dL (p = 0.4), and -47 mg/dL (IQR -87; -4) for baseline TC >300 mg/dL (p<0.01). No significant changes in liver enzymes or bilirubin were observed. SQV treatment was discontinued in 22% of patients, 6% due to side effects.
Conclusions: these data confirm the efficacy and tolerability of SQV/r in PI-experienced, SQV-naive patients treated in a real-life clinical setting. Of particular relevance are the improvements in triglycerides and TC levels observed in patients with baseline grade III-IV elevations.
Figures

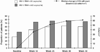
References
-
- Calza L, Manfredi R, Chiodo F. Dyslipidaemia associated with antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004;53(1):10–14. Review. - PubMed
-
- DAD Study Group. Friis-Møller N, Reiss P, Sabin CA, Weber R, Monforte A, El-Sadr W, Thiébaut R, De Wit S, Kirk O, Fontas E, Law MG, Phillips A, Lundgren JD. Class of antiretroviral drugs and the risk of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(17):1723–1735. - PubMed
-
- Walmsley S, Cheung AM, Fantus G, Gough K, Smaill F, Azad, Diong C, Raboud J. A prospective study of body fat redistribution, lipid, and glucose parameters in HIV-infected patients initiating combination antiretroviral therapy. HIV Clin Trials. 2008;9(5):314–323. doi: 10.1310/hct0905-314. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Palacios R, Merchante N, Macias J, González M, Castillo J, Ruiz J, Márquez M, Gómez-Mateos J, Pineda JA, Santos J. Incidence of and risk factors for insulin resistance in treatment-naïve HIV-infected patients 48 weeks after starting highly active antiretroviral therapy. Antivir Ther. 2006;11(4):529–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

