Individual lysine acetylations on the N terminus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae H2A.Z are highly but not differentially regulated
- PMID: 20952395
- PMCID: PMC3000967
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.185967
Individual lysine acetylations on the N terminus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae H2A.Z are highly but not differentially regulated
Abstract
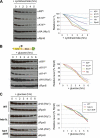
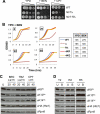
The multi-functional histone variant Htz1 (Saccharomyces cerevisiae H2A.Z) is acetylated on up to four N-terminal lysines at positions 3, 8, 10, and 14. It has thus been posited that specific acetylated forms of the histone could regulate distinct roles. Antibodies against Htz1-K8(Ac), -K10(Ac), and -K14(Ac) show that all three modifications are added by Esa1 acetyltransferase and removed by Hda1 deacetylase. Completely unacetylatable htz1 alleles exhibit widespread interactions in genome scale genetic screening. However, singly mutated (e.g. htz1-K8R) or singly acetylable (e.g. the triple mutant htz1-K3R/K10R/K14R) alleles show no significant defects in these analyses. This suggests that the N-terminal acetylations on Htz1 are internally redundant. Further supporting this proposal, each acetylation decays with similar kinetics when Htz1 transcription is repressed, and proteomic screening did not find a single condition in which one Htz1(Ac) was differentially regulated. However, whereas the individual acetylations on Htz1 may be redundant, they are not dispensable. Completely unacetylatable htz1 alleles display genetic interactions and phenotypes in common with and distinct from htz1Δ. In addition, each Htz1 N-terminal lysine is deacetylated by Hda1 in response to benomyl and reacetylated when this agent is removed. Such active regulation suggests that acetylation plays a significant role in Htz1 function.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Acetylation of H2AZ Lys 14 is associated with genome-wide gene activity in yeast.Genes Dev. 2006 Mar 15;20(6):711-22. doi: 10.1101/gad.1395506. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16543223 Free PMC article.
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae histone H2A variant Htz1 is acetylated by NuA4.Genes Dev. 2006 Mar 15;20(6):660-5. doi: 10.1101/gad.1388106. Genes Dev. 2006. PMID: 16543219 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide dynamics of Htz1, a histone H2A variant that poises repressed/basal promoters for activation through histone loss.Cell. 2005 Oct 21;123(2):219-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.036. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16239141 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in gene regulation.Bioessays. 1998 Aug;20(8):615-26. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199808)20:8<615::AID-BIES4>3.0.CO;2-H. Bioessays. 1998. PMID: 9780836 Review.
-
Post-translational lysine ac(et)ylation in health, ageing and disease.Biol Chem. 2021 Aug 23;403(2):151-194. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2021-0139. Print 2022 Jan 27. Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34433238 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-translational modifications of the histone variant H2AZ.Stem Cell Res. 2014 Jan;12(1):289-95. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Stem Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24316985 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
The Role of the Histone Variant H2A.Z in Metazoan Development.J Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 1;10(3):28. doi: 10.3390/jdb10030028. J Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35893123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The histone variant H2A.Z in gene regulation.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019 Jun 14;12(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13072-019-0274-9. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019. PMID: 31200754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights Into the Function of the NuA4 Complex in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Feb 21;11:125. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00125. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32153620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-resolution network biology: connecting sequence with function.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 Dec;14(12):865-79. doi: 10.1038/nrg3574. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 24197012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

