Chromatin and DNA methylation dynamics during retinoic acid-induced RET gene transcriptional activation in neuroblastoma cells
- PMID: 20952403
- PMCID: PMC3064803
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq864
Chromatin and DNA methylation dynamics during retinoic acid-induced RET gene transcriptional activation in neuroblastoma cells
Abstract
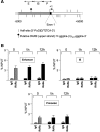
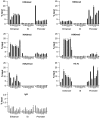
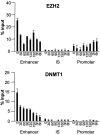
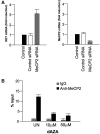
Although it is well known that RET gene is strongly activated by retinoic acid (RA) in neuroblastoma cells, the mechanisms underlying such activation are still poorly understood. Here we show that a complex series of molecular events, that include modifications of both chromatin and DNA methylation state, accompany RA-mediated RET activation. Our results indicate that the primary epigenetic determinants of RA-induced RET activation differ between enhancer and promoter regions. At promoter region, the main mark of RET activation was the increase of H3K4me3 levels while no significant changes of the methylation state of H3K27 and H3K9 were observed. At RET enhancer region a bipartite chromatin domain was detected in unstimulated cells and a prompt demethylation of H3K27me3 marked RET gene activation upon RA exposure. Moreover, ChIP experiments demonstrated that EZH2 and MeCP2 repressor complexes were associated to the heavily methylated enhancer region in the absence of RA while both complexes were displaced during RA stimulation. Finally, our data show that a demethylation of a specific CpG site at the enhancer region could favor the displacement of MeCP2 from the heavily methylated RET enhancer region providing a novel potential mechanism for transcriptional regulation of methylated RA-regulated loci.
Figures


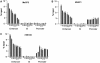

Similar articles
-
Epigenetic regulatory mechanisms distinguish retinoic acid-mediated transcriptional responses in stem cells and fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 7;285(19):14534-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115345. Epub 2010 Mar 15. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20231276 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin changes in dicer-deficient mouse embryonic stem cells in response to retinoic acid induced differentiation.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 9;8(9):e74556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074556. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040281 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone induces a putative repressor complex and chromatin modifications in the CRH promoter.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Jul;27(7):1142-52. doi: 10.1210/me.2013-1079. Epub 2013 May 13. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23671328 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation in human melanoma: past and future.Epigenetics. 2015;10(2):103-21. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2014.1003746. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 25587943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of skin: focus on the Polycomb complex.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Jul;69(13):2161-2172. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0920-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22314499 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation and Nutritional Science for Programs/Policies and Interpretation of Research Evidence (INSPIRE).J Nutr. 2015 May;145(5):1039S-1108S. doi: 10.3945/jn.114.194571. Epub 2015 Apr 1. J Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25833893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted DNA methylation by homology-directed repair in mammalian cells. Transcription reshapes methylation on the repaired gene.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(2):804-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt920. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24137009 Free PMC article.
-
A novel bidirectional interaction between endothelin-3 and retinoic acid in rat enteric nervous system precursors.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 9;8(9):e74311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074311. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040226 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-autonomous retinoic acid receptor signaling has stage-specific effects on mouse enteric nervous system.JCI Insight. 2021 May 24;6(10):e145854. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.145854. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 33848271 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Vitamin A Status as a Risk Factor of Hirschsprung Disease in the Child.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2023 Sep 1;14(9):e00619. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000619. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37490568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mark M, Ghyselinck NB, Chambon P. Function of retinoid nuclear receptors: lessons from genetic and pharmacological dissections of the retinoic acid signaling pathway during mouse embryogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2006;46:451–480. - PubMed
-
- Means AL, Gudas LJ. The roles of retinoids in vertebrate development. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995;64:201–233. - PubMed
-
- Mongan NP, Gudas LJ. Diverse actions of retinoid receptors in cancer prevention and treatment. Differentiation. 2007;75:853–870. - PubMed
-
- Germain P, Chambon P, Eichele G, Evans RM, Lazar MA, Leid M, De Lera AR, Lotan R, Mangelsdorf DJ, Gronemeyer H. International Union of Pharmacology. LX. Retinoic Acid Receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006;58:712–725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

