Inhibition of ALK, PI3K/MEK, and HSP90 in murine lung adenocarcinoma induced by EML4-ALK fusion oncogene
- PMID: 20952506
- PMCID: PMC3043107
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1671
Inhibition of ALK, PI3K/MEK, and HSP90 in murine lung adenocarcinoma induced by EML4-ALK fusion oncogene
Abstract
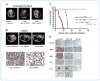
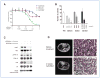
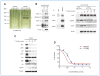
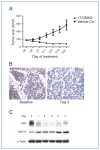
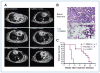
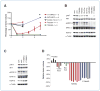
Genetic rearrangements of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) kinase occur in 3% to 13% of non-small cell lung cancer patients and rarely coexist with KRASor EGFR mutations. To evaluate potential treatment strategies for lung cancers driven by an activated EML4-ALK chimeric oncogene, we generated a genetically engineered mouse model that phenocopies the human disease where this rearranged gene arises. In this model, the ALK kinase inhibitor TAE684 produced greater tumor regression and improved overall survival compared with carboplatin and paclitaxel, representing clinical standard of care. 18F-FDG-PET-CT scans revealed almost complete inhibition of tumor metabolic activity within 24 hours of TAE684 exposure. In contrast, combined inhibition of the PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK1/2 pathways did not result in significant tumor regression. We identified EML4-ALK in complex with multiple cellular chaperones including HSP90. In support of a functional reliance, treatment with geldanamycin-based HSP90 inhibitors resulted in rapid degradation of EML4-ALK in vitro and substantial, albeit transient, tumor regression in vivo. Taken together, our findings define a murine model that offers a reliable platform for the preclinical comparison of combinatorial treatment approaches for lung cancer characterized by ALK rearrangement.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, Dittmer KG, Shapiro DN, Saltman DL, et al. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science. 1994;263:1281–4. - PubMed
-
- Shinmura K, Kageyama S, Tao H, Bunai T, Suzuki M, Kamo T, et al. EML4-ALK fusion transcripts, but no NPM-, TPM3-, CLTC-, ATIC-, or TFG-ALK fusion transcripts, in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Lung Cancer. 2008;61:163–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

