Resveratrol, a red wine polyphenol, suppresses pancreatic cancer by inhibiting leukotriene A₄hydrolase
- PMID: 20952510
- PMCID: PMC4872628
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2858
Resveratrol, a red wine polyphenol, suppresses pancreatic cancer by inhibiting leukotriene A₄hydrolase
Abstract
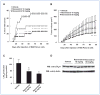
The anticancer effects of red wine have attracted considerable attention. Resveratrol (3,5,4'-trihydroxy-trans -stilbene) is a well-known polyphenolic compound of red wine with cancer chemopreventive activity. However, the basis for this activity is unclear. We studied leukotriene A(4) hydrolase (LTA(4)H) as a relevant target in pancreatic cancer. LTA(4)H knockdown limited the formation of leukotriene B(4) (LTB(4)), the enzymatic product of LTA(4)H, and suppressed anchorage-independent growth of pancreatic cancer cells. An in silico shape similarity algorithm predicted that LTA(4)H might be a potential target of resveratrol. In support of this idea, we found that resveratrol directly bound to LTA(4)H in vitro and in cells and suppressed proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of pancreatic cancer by inhibiting LTB(4) production and expression of the LTB(4) receptor 1 (BLT(1)). Notably, resveratrol exerted relatively stronger inhibitory effects than bestatin, an established inhibitor of LTA(4)H activity, and the inhibitory effects of resveratrol were reduced in cells where LTA(4)H was suppressed by shRNA-mediated knockdown. Importantly, resveratrol inhibited tumor formation in a xenograft mouse model of human pancreatic cancer by inhibiting LTA(4)H activity. Our findings identify LTA(4)H as a functionally important target for mediating the anticancer properties of resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

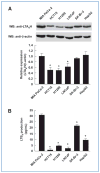
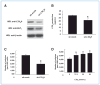
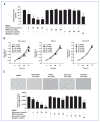
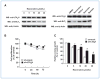
References
-
- Damianaki A, Bakogeorgou E, Kampa M, Notas G, Hatzoglou A, Panagiotou S, et al. Potent inhibitory action of red wine polyphenols on human breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 2000;78:429–41. - PubMed
-
- German JB, Walzem RL. The health benefits of wine. Annu Rev Nutr. 2000;20:561–93. - PubMed
-
- Kris-Etherton PM, Hecker KD, Bonanome A, Coval SM, Binkoski AE, Hilpert KF, et al. Bioactive compounds in foods: their role in the prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer. Am J Med. 2002;113(Suppl 9B):71S–88S. - PubMed
-
- Kalra N, Roy P, Prasad S, Shukla Y. Resveratrol induces apoptosis involving mitochondrial pathways in mouse skin tumorigenesis. Life Sci. 2008;82:348–58. - PubMed
-
- Jang M, Cai L, Udeani GO, Slowing KV, Thomas CF, Beecher CW, et al. Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes. Science. 1997;275:218–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

