Induced pluripotency: history, mechanisms, and applications
- PMID: 20952534
- PMCID: PMC2956203
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1963910
Induced pluripotency: history, mechanisms, and applications
Abstract
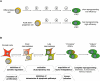
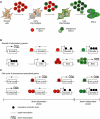
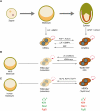
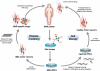
The generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from somatic cells demonstrated that adult mammalian cells can be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state by the enforced expression of a few embryonic transcription factors. This discovery has raised fundamental questions about the mechanisms by which transcription factors influence the epigenetic conformation and differentiation potential of cells during reprogramming and normal development. In addition, iPSC technology has provided researchers with a unique tool to derive disease-specific stem cells for the study and possible treatment of degenerative disorders with autologous cells. In this review, we summarize the progress that has been made in the iPSC field over the last 4 years, with an emphasis on understanding the mechanisms of cellular reprogramming and its potential applications in cell therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Aasen T, Raya A, Barrero MJ, Garreta E, Consiglio A, Gonzalez F, Vassena R, Bilic J, Pekarik V, Tiscornia G, et al. 2008. Efficient and rapid generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human keratinocytes. Nat Biotechnol 26: 1276–1284 - PubMed
-
- Akao Y, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T 2006. let-7 microRNA functions as a potential growth suppressor in human colon cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull 29: 903–906 - PubMed
-
- Aoi T, Yae K, Nakagawa M, Ichisaka T, Okita K, Takahashi K, Chiba T, Yamanaka S 2008. Generation of pluripotent stem cells from adult mouse liver and stomach cells. Science 321: 699–702 - PubMed
-
- Aoki T, Ohnishi H, Oda Y, Tadokoro M, Sasao M, Kato H, Hattori K, Ohgushi H 2010. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human adipose-derived stem cells without c-MYC. Tissue Eng Part A 16: 2197–2206 - PubMed
-
- Araki R, Jincho Y, Hoki Y, Nakamura M, Tamura C, Ando S, Kasama Y, Abe M 2010. Conversion of ancestral fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 28: 213–220 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
