A novel approach to in vivo mitral valve stress analysis
- PMID: 20952665
- PMCID: PMC3774186
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00370.2010
A novel approach to in vivo mitral valve stress analysis
Abstract
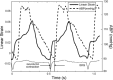
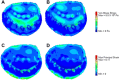
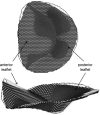
Three-dimensional (3-D) echocardiography allows the generation of anatomically correct and time-resolved geometric mitral valve (MV) models. However, as imaged in vivo, the MV assumes its systolic geometric configuration only when loaded. Customarily, finite element analysis (FEA) is used to predict material stress and strain fields rendered by applying a load on an initially unloaded model. Therefore, this study endeavors to provide a framework for the application of in vivo MV geometry and FEA to MV physiology, pathophysiology, and surgical repair. We hypothesize that in vivo MV geometry can be reasonably used as a surrogate for the unloaded valve in computational (FEA) simulations, yielding reasonable and meaningful stress and strain magnitudes and distributions. Three experiments were undertaken to demonstrate that the MV leaflets are relatively nondeformed during systolic loading: 1) leaflet strain in vivo was measured using sonomicrometry in an ovine model, 2) hybrid models of normal human MVs as constructed using transesophageal real-time 3-D echocardiography (rt-3DE) were repeatedly loaded using FEA, and 3) serial rt-3DE images of normal human MVs were used to construct models at end diastole and end isovolumic contraction to detect any deformation during isovolumic contraction. The average linear strain associated with isovolumic contraction was 0.02 ± 0.01, measured in vivo with sonomicrometry. Repeated loading of the hybrid normal human MV demonstrated little change in stress or geometry: peak von Mises stress changed by <4% at all locations on the anterior and posterior leaflets. Finally, the in vivo human MV deformed minimally during isovolumic contraction, as measured by the mean absolute difference calculated over the surfaces of both leaflets between serial MV models: 0.53 ± 0.19 mm. FEA modeling of MV models derived from in vivo high-resolution truly 3-D imaging is reasonable and useful for stress prediction in MV pathologies and repairs.
Figures
References
-
- Avanzani A. A computational procedure for prediction of structural effects of edge-to-edge repair on mitral valve. J Biomech Eng 130: 031015, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Cochran RP, Kunzelman KS. Effect of papillary muscle position on mitral valve function: relationship to homografts. Ann Thorac Surg 66: S155–S161, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Dal Pan F, Donzella G, Fucci C, Schreiber M. Structural effects of an innovative surgical technique to repair heart valve defects. J Biomech 38: 2460–2471, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Einstein DR, Kunzelman KS, Reinhall PG, Nicosia MA, Cochran RP. Non-linear fluid-coupled computational model of the mitral valve. J Heart Valve Dis 14: 376–385, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Gorman JH, 3rd, Gupta KB, Streicher JT, Gorman RC, Jackson BM, Ratcliffe MB, Bogen DK, Edmunds LH., Jr Dynamic three-dimensional imaging of the mitral valve and left ventricle by rapid sonomicrometry array localization. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 112: 712–726, 1996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

