Circadian regulation of cardiovascular function: a role for vasoactive intestinal peptide
- PMID: 20952671
- PMCID: PMC4116412
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00190.2010
Circadian regulation of cardiovascular function: a role for vasoactive intestinal peptide
Abstract
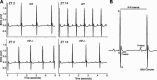
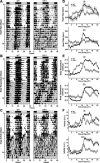
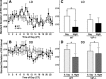
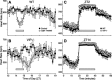
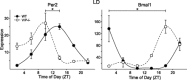
The circadian system, driven by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), regulates properties of cardiovascular function. The dysfunction of this timing system can result in cardiac pathology. The neuropeptide vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is crucial for circadian rhythms in a number of biological processes including SCN electrical activity and wheel running behavior. Anatomic evidence indicates that SCN neurons expressing VIP are well positioned to drive circadian regulation of cardiac function through interactions with the autonomic centers. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that loss of VIP would result in circadian deficits in heart rate (HR) and clock gene expression in cardiac tissue. We implanted radiotelemetry devices into VIP-deficient mice and wild-type (WT) controls and continuously recorded HR, body temperature, and cage activity in freely moving mice. Under light-dark conditions, VIP-deficient mice displayed weak rhythms in HR, body temperature, and cage activity, with onsets that were advanced in phase compared with WT mice. Similarly, clock gene expression in cardiac tissue was rhythmic but phase advanced in mutant mice. In constant darkness, the normal circadian rhythms in HR were lost in VIP-deficient mice; however, most mutant mice continued to exhibit circadian rhythms of body temperature with shortened free-running period. The loss of VIP altered, but did not abolish, autonomic regulation of HR. Analysis of the echocardiograms did not find any evidence for a loss of cardiac function in VIP-deficient mice, and the size of the hearts did not differ between genotypes. These results demonstrate that VIP is an important regulator of physiological circadian rhythmicity in the heart.
Figures
References
-
- Accili EA, Redaelli G, DiFrancesco D. Activation of the hyperpolarization-activated current (If) in sino-atrial node myocytes of the rabbit by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Pflugers Arch 431: 803–805, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Bechtold DA, Brown TM, Luckman SM, Piggins HD. Metabolic rhythm abnormalities in mice lacking VIP-VPAC2 signaling. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294: R344–R351, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Bray MS, Shaw CA, Moore MW, Garcia RA, Zanquetta MM, Durgan DJ, Jeong WJ, Tsai JY, Bugger H, Zhang D, Rohrwasser A, Rennison JH, Dyck JR, Litwin SE, Hardin PE, Chow CW, Chandler MP, Abel ED, Young ME. Disruption of the circadian clock within the cardiomyocyte influences myocardial contractile function, metabolism, and gene expression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294: H1036–H1047, 2008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

