A ligand for CD5 is CD5
- PMID: 20952682
- PMCID: PMC2996635
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903823
A ligand for CD5 is CD5
Abstract
Recognition by scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domains on membrane proteins regulates innate and adaptive immune responses. Two receptors expressed primarily on T cells, CD5 and CD6, are linked genetically and are structurally similar, both containing three scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domains in their extracellular regions. A specific cell surface interaction for CD5 has been difficult to define at the molecular level because of the susceptibility of CD5 protein to denaturation. By using soluble CD5 purified at neutral pH to preserve biological activity, we show that CD5 mediates species-specific homophilic interactions. CD5 domain 1 only is involved in the interaction. CD5 mAbs that have functional effects in humans, rats, and mice block homophilic binding. Ag-specific responses by mouse T cells in vitro were increased when engagement of human CD5 domain 1 was inhibited by mutation or by IgG or Fab fragment from a CD5 mAb. This showed that homophilic binding results in productive engagement. Enhancement of polyclonal immune responses of rat lymph node cells by a Fab fragment from a CD5 mAb shown to block homophilic interactions provided evidence that the extracellular region of CD5 regulates inhibition in normal cells. These biochemical and in vitro functional assays provide evidence that the extracellular region of CD5 regulates immunity through species-specific homophilic interactions.
Figures

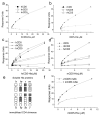
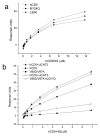

References
-
- Aruffo A, Bowen MA, Patel DD, Haynes BF, Starling GC, Gebe JA, Bajorath J. CD6-ligand interactions: a paradigm for SRCR domain function? Immunol. Today. 1997;18:498–504. - PubMed
-
- Sarrias MR, Gronlund J, Padilla O, Madsen J, Holmskov U, Lozano F. The Scavenger Receptor Cysteine-Rich (SRCR) domain: an ancient and highly conserved protein module of the innate immune system. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2004;24:1–37. - PubMed
-
- Bhandoola A, Bosselut R, Yu Q, Cowan ML, Feigenbaum L, Love PE, Singer A. CD5-mediated inhibition of TCR signaling during intrathymic selection and development does not require the CD5 extracellular domain. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002;32:1811–1817. - PubMed
-
- Pena-Rossi C, Zuckerman LA, Strong J, Kwan J, Ferris W, Chan S, Tarakhovsky A, Beyers AD, Killeen N. Negative regulation of CD4 lineage development and responses by CD5. J. Immunol. 1999;163:6494–6501. - PubMed
-
- Tarakhovsky A, Kanner SB, Hombach J, Ledbetter JA, Muller W, Killeen N, Rajewsky K. A role for CD5 in TCR-mediated signal transduction and thymocyte selection. Science. 1995;269:535–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

