Opposing roles for HIF-1α and HIF-2α in the regulation of angiogenesis by mononuclear phagocytes
- PMID: 20952691
- PMCID: PMC3037754
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-01-261792
Opposing roles for HIF-1α and HIF-2α in the regulation of angiogenesis by mononuclear phagocytes
Abstract
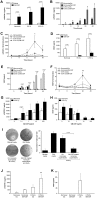
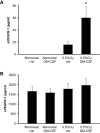
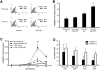
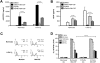
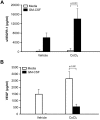
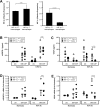
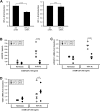
Macrophages contribute to tumor growth through the secretion of the proangiogenic molecule vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). We previously observed that monocytes treated with the cytokine granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) produce a soluble form of the VEGF receptor-1 (sVEGFR-1), which neutralizes VEGF biologic activity. The VEGF and VEGFR-1 promoters both contain a hypoxia regulatory element, which binds the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) transcription factors under hypoxic conditions. Based on this observation, we examined VEGF and sVEGFR-1 production from monocytes cultured at various O(2) concentrations. The amount of sVEGFR-1 production observed from GM-CSF-treated monocytes increased with decreasing levels of O(2). This sVEGFR-1 was biologically active and sequestered VEGF. To evaluate the role of the HIFs in sVEGFR-1 production, we used macrophages with a genetic deletion of HIF-1α. HIF-1α(-/-) macrophages cultured with GM-CSF at hypoxia secreted diminished amounts of VEGF compared with HIF-1α(+/+) macrophages, whereas sVEGFR-1 secretion was unaffected. In contrast, siRNA-mediated knockdown of HIF-2α inhibited the production of sVEGFR-1 in response to GM-CSF and low O(2), whereas VEGF production was unaffected. These studies suggest that hypoxia, generally thought to promote angiogenesis, can induce antiangiogenic behavior from macrophages within a GM-CSF-rich environment. Furthermore, these results suggest specific and independent roles for HIF-1α and HIF-2α in hypoxic macrophages.
Figures
References
-
- Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D, Keshet E. Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 1992;359(6398):843–845. - PubMed
-
- Dachs GU, Patterson AV, Firth JD, et al. Targeting gene expression to hypoxic tumor cells. Nat Med. 1997;3(5):515–520. - PubMed
-
- Blancher C, Moore JW, Talks KL, Houlbrook S, Harris AL. Relationship of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-2alpha expression to vascular endothelial growth factor induction and hypoxia survival in human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2000;60(24):7106–7113. - PubMed
-
- Choi SM, Oh H, Park H. Microarray analyses of hypoxia-regulated genes in an aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (Arnt)-dependent manner. FEBS J. 2008;275(22):5618–5634. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

