Targeting CYP450 modulation to decrease the risk of induced cataract in the experimental model
- PMID: 20952829
- PMCID: PMC2993975
- DOI: 10.4103/0301-4738.71676
Targeting CYP450 modulation to decrease the risk of induced cataract in the experimental model
Abstract
Background: Diabetes is one of the major causes of cataract. Some drugs prescribed for the treatment of diabetes are the modulators of CYP450, which may alter the risk of cataract.
Objective: To study the effect of CYP450 modulation in galactosemic cataract.
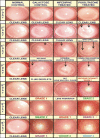
Materials and methods: Male Sprague-Dawley suckling rats were allotted to four groups (n = 6), as follows: Group 1: Normal control, Group 2: Galactose control, Group 3: CYP450 inhibitor pretreated and Group 4: CYP450 inducer pretreated. Cataract was induced in animals of all groups except group 1 by feeding them galactose (50%), 21 days after parturition. From the eighteenth day of life, CYP450 inhibitor (nifedipine; 8.1 mg/kg) and CYP450 inducer (pioglitazone; 3.8 mg/kg) were given orally to groups 3 and 4, respectively. The maturation pattern of the cataract was observed by an operating microscope, every third day. Biochemical changes in the lenses of all groups, for example, CYP450 activity expressed as ΅M NADPH oxidized / unit time, alterations in the levels of total proteins, soluble proteins, and reduced glutathione (GSH) following the induction of cataract, were estimated.
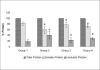
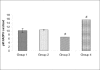
Results: The microscopic examination of the lenses indicated that CYP450 inhibitor pre-treatment delayed (fourteenth day) the occurrence of cataract, while CYP450 inducer pretreatment demonstrated an early (ninth day) cataract as compared to galactose control rats (twelfth day). A significant decrease and increase in CYP450 activity was observed with the CYP450 inhibitor and inducer pre-treatment, respectively. There was no alteration in the GSH level, but a significant increase in total and soluble protein was found in groups 3 and 4 as compared to group 2.
Conclusion: CYP450 may have a role in the initiation of cataract without any effect on the maturation pattern, as revealed by the delayed occurrence of cataract with the CYP450 inhibitor and an early onset of cataract with the CYP450 inducer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Inferences from targeting CYP450 modulation to decrease the risk of induced cataract in the experimental model?Indian J Ophthalmol. 2011 Sep-Oct;59(5):403. doi: 10.4103/0301-4738.83626. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21836356 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Role of Cytochrome Modulators in Altering the Occurrence of Cataract in Rats.J Clin Diagn Res. 2015 Jul;9(7):FF05-7. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/12411.6216. Epub 2015 Jul 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015. PMID: 26393141 Free PMC article.
-
Inferences from targeting CYP450 modulation to decrease the risk of induced cataract in the experimental model?Indian J Ophthalmol. 2011 Sep-Oct;59(5):403. doi: 10.4103/0301-4738.83626. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21836356 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effects of magnesium taurate on the onset and progression of galactose-induced experimental cataract: in vivo and in vitro evaluation.Exp Eye Res. 2013 May;110:35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.02.011. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23428743
-
The unfolded protein response in lens epithelial cells from galactosemic rat lenses.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Sep;47(9):3951-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-0193. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 16936110
-
Effect of curcumin on galactose-induced cataractogenesis in rats.Mol Vis. 2003 Jun 9;9:223-30. Mol Vis. 2003. PMID: 12802258
Cited by
-
Effect of rifampicin and erythromycin on the initiation of galactose induced cataract in rats.J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2012 Oct;3(4):330-2. doi: 10.4103/0976-500X.103693. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2012. PMID: 23326107 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Role of Cytochrome Modulators in Altering the Occurrence of Cataract in Rats.J Clin Diagn Res. 2015 Jul;9(7):FF05-7. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/12411.6216. Epub 2015 Jul 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015. PMID: 26393141 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress in Cataract Formation: Is There a Treatment Approach on the Horizon?Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 16;13(10):1249. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101249. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inferences from targeting CYP450 modulation to decrease the risk of induced cataract in the experimental model?Indian J Ophthalmol. 2011 Sep-Oct;59(5):403. doi: 10.4103/0301-4738.83626. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21836356 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A simple and stable galactosemic cataract model for rats.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Aug 15;8(8):12874-81. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26550203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sasaki K, Karino K, Kojima M, Sakamoto Y, Takizawa A, Zeinuddin D, et al. Cataract survey in the local area using photographic documentation. Dev Ophthalmol. 1987;15:28–36. - PubMed
-
- McCarty CA, Nanjan MB, Taylor HR. Attributable risk estimates for cataract to prioritize medical and public health action. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:3720–5. - PubMed
-
- Esteves JF, Dal Pizzol MM, Sccoco CA, Roggia MF, Milano SB, Guarienti JA, et al. Cataract and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;82:324–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

