Maternal mRNA deadenylation and decay by the piRNA pathway in the early Drosophila embryo
- PMID: 20953170
- PMCID: PMC4505748
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09465
Maternal mRNA deadenylation and decay by the piRNA pathway in the early Drosophila embryo
Abstract
Piwi-associated RNAs (piRNAs), a specific class of 24- to 30-nucleotide-long RNAs produced by the Piwi-type of Argonaute proteins, have a specific germline function in repressing transposable elements. This repression is thought to involve heterochromatin formation and transcriptional and post-transcriptional silencing. The piRNA pathway has other essential functions in germline stem cell maintenance and in maintaining germline DNA integrity. Here we uncover an unexpected function of the piRNA pathway in the decay of maternal messenger RNAs and in translational repression in the early embryo. A subset of maternal mRNAs is degraded in the embryo at the maternal-to-zygotic transition. In Drosophila, maternal mRNA degradation depends on the RNA-binding protein Smaug and the deadenylase CCR4, as well as the zygotic expression of a microRNA cluster. Using mRNA encoding the embryonic posterior morphogen Nanos (Nos) as a paradigm to study maternal mRNA decay, we found that CCR4-mediated deadenylation of nos depends on components of the piRNA pathway including piRNAs complementary to a specific region in the nos 3' untranslated region. Reduced deadenylation when piRNA-induced regulation is impaired correlates with nos mRNA stabilization and translational derepression in the embryo, resulting in head development defects. Aubergine, one of the Argonaute proteins in the piRNA pathway, is present in a complex with Smaug, CCR4, nos mRNA and piRNAs that target the nos 3' untranslated region, in the bulk of the embryo. We propose that piRNAs and their associated proteins act together with Smaug to recruit the CCR4 deadenylation complex to specific mRNAs, thus promoting their decay. Because the piRNAs involved in this regulation are produced from transposable elements, this identifies a direct developmental function for transposable elements in the regulation of gene expression.
Figures

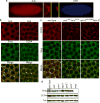
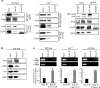
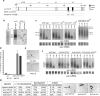
Comment in
-
Development: Transposon-derived small RNAs control patterning.Nat Rev Genet. 2010 Dec;11(12):816. doi: 10.1038/nrg2912. Epub 2010 Nov 3. Nat Rev Genet. 2010. PMID: 21045867 No abstract available.
-
Gene expression: Patterning by piRNAs.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;11(12):820. doi: 10.1038/nrm3009. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 21068768 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vagin VV, et al. A distinct small RNA pathway silences selfish genetic elements in the germline. Science. 2006;313:320–4. - PubMed
-
- Brennecke J, et al. Discrete small RNA-generating loci as master regulators of transposon activity in Drosophila. Cell. 2007;128:1089–103. - PubMed
-
- Yin H, Lin H. An epigenetic activation role of Piwi and a Piwi-associated piRNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 2007;450:304–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

