DNA-controlled assembly of a NaTl lattice structure from gold nanoparticles and protein nanoparticles
- PMID: 20953184
- PMCID: PMC4006348
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat2877
DNA-controlled assembly of a NaTl lattice structure from gold nanoparticles and protein nanoparticles
Abstract
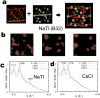
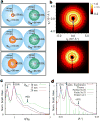
The formation of diamond structures from tailorable building blocks is an important goal in colloidal crystallization because the non-compact diamond lattice is an essential component of photonic crystals for the visible-light range. However, designing nanoparticle systems that self-assemble into non-compact structures has proved difficult. Although several methods have been proposed, single-component nanoparticle assembly of a diamond structure has not been reported. Binary systems, in which at least one component is arranged in a diamond lattice, provide alternatives, but control of interparticle interactions is critical to this approach. DNA has been used for this purpose in a number of systems. Here we show the creation of a non-compact lattice by DNA-programmed crystallization using surface-modified Qβ phage capsid particles and gold nanoparticles, engineered to have similar effective radii. When combined with the proper connecting oligonucleotides, these components form NaTl-type colloidal crystalline structures containing interpenetrating organic and inorganic diamond lattices, as determined by small-angle X-ray scattering. DNA control of assembly is therefore shown to be compatible with particles possessing very different properties, as long as they are amenable to surface modification.
Figures


Comment in
-
Nanoparticle assembly: made to order.Nat Mater. 2010 Nov;9(11):885-7. doi: 10.1038/nmat2892. Nat Mater. 2010. PMID: 20966933 No abstract available.
References
-
- Joannopoulos JD, Johnson SG, Winn JN, Meade RD. Photonic Crystals: Molding the Flow of Light. Princeton University Press; 2008.
-
- Norris DJ. Photonic Crystals: A view of the future. Nat Mater. 2007;6:177–178. - PubMed
-
- Yablonovitch E. Inhibited Spontaneous Emission In Solid-State Physics And Electronics. Phys Rev Lett. 1987;58:2059–2062. - PubMed
-
- John S. Strong Localization Of Photons In Certain Disordered Dielectric Superlattices. Phys Rev Lett. 1987;58:2486–2489. - PubMed
-
- Ho KM, Chan CT, Soukoulis CM. Existence of a photonic gap in periodic dielectric structures. Phys Rev Lett. 1990;65:3152–3155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

