IL-35-mediated induction of a potent regulatory T cell population
- PMID: 20953201
- PMCID: PMC3008395
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1952
IL-35-mediated induction of a potent regulatory T cell population
Abstract
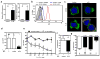
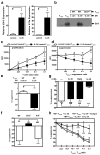
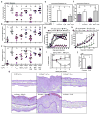
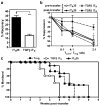
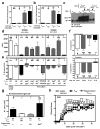
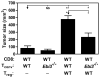
Regulatory T cells (T(reg) cells) have a critical role in the maintenance of immunological self-tolerance. Here we show that treatment of naive human or mouse T cells with IL-35 induced a regulatory population, which we call 'iT(R)35 cells', that mediated suppression via IL-35 but not via the inhibitory cytokines IL-10 or transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). We found that iT(R)35 cells did not express or require the transcription factor Foxp3, and were strongly suppressive and stable in vivo. T(reg) cells induced the generation of iT(R)35 cells in an IL-35- and IL-10-dependent manner in vitro and induced their generation in vivo under inflammatory conditions in intestines infected with Trichuris muris and within the tumor microenvironment (B16 melanoma and MC38 colorectal adenocarcinoma), where they contributed to the regulatory milieu. Thus, iT(R)35 cells constitute a key mediator of infectious tolerance and contribute to T(reg) cell-mediated tumor progression. Furthermore, iT(R)35 cells generated ex vivo might have therapeutic utility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Regulatory ripples.Nat Immunol. 2010 Dec;11(12):1077-8. doi: 10.1038/ni1210-1077. Nat Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21079629 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fontenot JD, et al. Regulatory T cell lineage specification by the forkhead transcription factor foxp3. Immunity. 2005;22:329–341. - PubMed
-
- Gavin MA, et al. Foxp3-dependent programme of regulatory T-cell differentiation. Nature. 2007;445:771–775. - PubMed
-
- Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003;299:1057–1061. - PubMed
-
- Shevach EM, et al. The lifestyle of naturally occurring CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:60–73. - PubMed
-
- Waldmann H, Adams E, Fairchild P, Cobbold S. Infectious tolerance and the long-term acceptance of transplanted tissue. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:301–313. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

