NKT cells in sepsis
- PMID: 20953368
- PMCID: PMC2952903
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/414650
NKT cells in sepsis
Abstract
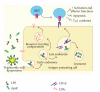
Sepsis is currently a leading cause of death in hospital intensive care units. Previous studies suggest that the pathophysiology of sepsis involves the hyperactivation of complex proinflammatory cascades that include the activation of various immune cells and the exuberant secretion of proinflammatory cytokines by these cells. Natural killer T-cells (NKTs) are a sublineage of T cells that share characteristics of conventional T cells and NK cells and bridge innate and adaptive immunity. More recently, NKT cells have been implicated in microbial immunity, including the onset of sepsis. Moreover, apolipoprotein E (apoE), a component of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, has been shown to be protective in endotoxemia and gram-negative infections in addition to its well-known role in lipid metabolism. Here, we will review the role of NKT cells in sepsis and septic shock, the immunoregulatory role of apoE in the host immune response to infection, and propose a mechanism for this immunoregulation.
Figures
References
-
- Balato A, Unutmaz D, Gaspari AA. Natural killer T cells: an unconventional t-cell subset with diverse effector and regulatory functions. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 2009;129(7):1628–1642. - PubMed
-
- Godfrey DI, Hammond KJL, Poulton LD, Smyth MJ, Baxter AG. NKT cells: facts, functions and fallacies. Immunology Today. 2000;21(11):573–583. - PubMed
-
- Godfrey DI, MacDonald HR, Kronenberg M, Smyth MJ, Van Kaer L. NKT cells: what’s in a name? Nature Reviews Immunology. 2004;4(3):231–237. - PubMed
-
- Beckman EM, Porcelli SA, Morita CT, Behar SM, Furlong ST, Brenner MB. Recognition of lipid antigen by CD1-restricted α β + T cells. Nature. 1994;372(6507):691–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

