Selective Th2 Upregulation by Crocus sativus: A Neutraceutical Spice
- PMID: 20953384
- PMCID: PMC2952317
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/639862
Selective Th2 Upregulation by Crocus sativus: A Neutraceutical Spice
Abstract
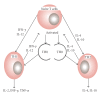
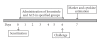
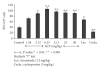
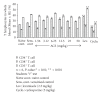
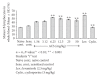
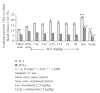
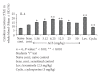
The immunomodulatory activity of an Indian neutraceutical spice, saffron (Crocus sativus) was studied on Th(1) and Th(2) limbs of the immune system. Oral administration of alcoholic extract of Crocus sativus (ACS) at graded dose levels from 1.56-50 mg/kg p.o. potentiated the Th(2) response of humoral immunity causing the significant increases in agglutinating antibody titre in mice at a dose of 6.25 mg/kg and an elevation of CD19(+) B cells and IL-4 cytokine, a signature cytokine of Th(2) pathway. Appreciable elevation in levels of IgG-1 and IgM antibodies of the primary and secondary immune response was observed. However, ACS showed no appreciable expression of the Th(1) cytokines IL-2 (growth factor for CD4(+) T cells) and IFN-γ (signature cytokine of Th(1) response). A significant modulation of immune reactivity was observed in all the animal models used. This paper represents the selective upregulation of the Th(2) response of the test material and suggests its use for subsequent selective Th(2) immunomodulation.
Figures



References
-
- Cooper EL, Ru B, Weng N. Earthworms: sources of antimicrobial and anticancer molecules. In: Cooper EL, Yamaguchi N, editors. Complementary and Alternative Approaches to Biomedicine. Dodrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2004. pp. 359–390.
-
- Cooper EL, Hrzenjak TM, Grdiša M. Alternative sources of fibrinolytic, anticoagulative, antimicrobial and anticancer molecules. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology. 2004;17(3):237–244. - PubMed
-
- Haefner B. Drugs from the deep: marine natural products as drug candidates. Drug Discovery Today. 2003;8(12):536–544. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

