Characterization of the Antidiabetic Role of Parkinsonia aculeata (Caesalpineaceae)
- PMID: 20953386
- PMCID: PMC2952319
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/692378
Characterization of the Antidiabetic Role of Parkinsonia aculeata (Caesalpineaceae)
Abstract
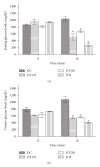
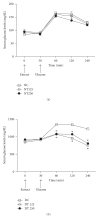
This paper reports the characterization of the antidiabetic role of a hydroethanolic extract from Parkinsonia aerial parts (HEPA), in normal and alloxan-induced diabetic rats, treated with HEPA (125 and 250 mg/kg; p.o.). Oral glucose tolerance test, acute oral toxicity test and preliminary phytochemical analyses were performed. The diabetic rats treated with HEPA showed a significant reduction in serum and urinary glucose, urinary urea and triglyceride levels, as compared to the diabetic untreated group. However, in the normal treated groups, a significant reduction was found only in serum triglyceride levels. In all treated diabetic groups, an improvement in hepatic glycogen was observed, as well as a decrease in liquid intake and urinary volume, and an enhancement in the weight of skeletal muscles (soleus and extensor digitorum longus), kidneys and epididymal adipose tissue. Nevertheless, body and liver weights were ameliorated only in the diabetic group treated with HEPA (250 mg/kg). Moreover, oral glucose tolerance was higher in animals treated with HEPA, while results also showed that HEPA could be considered toxicologically safe. Phytochemical analysis revealed the presence of tanins, flavonoids and steroids in HEPA. In conclusion, P. aculeata presents an antidiabetic activity and other beneficial effects that ameliorate diabetes and associated complications.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Treatment with Parkinsonia aculeata combats insulin resistance-induced oxidative stress through the increase in PPARγ/CuZn-SOD axis expression in diet-induced obesity mice.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Aug;419(1-2):93-101. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2753-7. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27372351
-
Parkinsonia aculeata aqueous extract fraction: biochemical studies in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 May 22;111(3):547-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.12.032. Epub 2007 Jan 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17276638
-
Parkinsonia aculeata (Caesalpineaceae) improves high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice through the enhancement of insulin signaling and mitochondrial biogenesis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 May 13;183:95-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.02.048. Epub 2016 Mar 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26940900
-
Polar fraction from Parkinsonia aculeata aerial parts extract improves imbalanced metabolic profile and reduces proinflammatory interleukin levels in white adipose tissue in obese rats induced by western diet.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jan 10;282:114557. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114557. Epub 2021 Sep 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34481874
-
Antidiabetic profiling, cytotoxicity and acute toxicity evaluation of aerial parts of Phragmites karka (Retz.).J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 24;270:113781. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113781. Epub 2021 Jan 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33421602
Cited by
-
Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Ethanolic Extract of Mirabilis jalapa L. Root on Normal and Diabetic Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:257374. doi: 10.1155/2012/257374. Epub 2012 Feb 27. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22474494 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic islet regeneration and some liver biochemical parameters of leaf extracts of Vitex doniana in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic albino rats.Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2014 Feb;4(2):124-30. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(14)60220-3. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2014. PMID: 25182283 Free PMC article.
-
Lectin from Crataeva tapia Bark Improves Tissue Damages and Plasma Hyperglycemia in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:869305. doi: 10.1155/2013/869305. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 24324521 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with Parkinsonia aculeata combats insulin resistance-induced oxidative stress through the increase in PPARγ/CuZn-SOD axis expression in diet-induced obesity mice.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Aug;419(1-2):93-101. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2753-7. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27372351
-
Evaluation of acute oral toxicity, embryotoxicity and cytotoxicity of the polar fraction of Parkinsonia aculeata aerial parts extract.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2020 Feb 21;9(1):19-27. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfz002. eCollection 2020 Feb. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2020. PMID: 32440335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang J, Armour T, Geiss LS, Engelgau MM. Obesity and diabetes: dual epidemics on the rise. Current Opinion in Endocrinology and Diabetes. 2005;12(2):174–180.
-
- Reimann M, Bonifacio E, Solimena M, et al. An update on preventive and regenerative therapies in diabetes mellitus. Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2009;121(3):317–331. - PubMed
-
- de Melo Junior EJM, Raposo MJ, Lisboa Neto JA, Diniz MFA, Marcelino Junior CAC, Sant’Ana AEG. Medicinal plants in the healing of dry socket in rats: microbiological and microscopic analysis. Phytomedicine. 2002;9(2):109–116. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

