KIOM-79 Prevents Lens Epithelial Cell Apoptosis and Lens Opacification in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats
- PMID: 20953387
- PMCID: PMC2952320
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/717921
KIOM-79 Prevents Lens Epithelial Cell Apoptosis and Lens Opacification in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats
Abstract
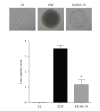
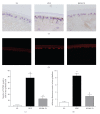
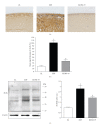
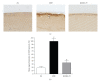
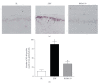
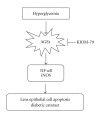
Damage of lens epithelial cells (LECs) has been implicated in cataract formation. The aim of this study was to investigate the protective effect of KIOM-79, a combination of four plant extracts, on LECs. We examined the levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) activation and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression in LECs during cataract development using the Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rat, an animal model of type 2 diabetes. KIOM-79 was orally administered by gavage to ZDF rats once a day for 13 weeks. Apoptosis was detected by TUNEL assay, and NF-κB activation and iNOS expression were studied by southwestern histochemistry and immunohistochemistry, respectively. In diabetic cataractous lenses, TUNEL-positive LECs were markedly increased 20-fold, and AGEs were highly accumulated (2.7-fold) in LECs. In addition, both NF-κB activation, and iNOS expression were significantly enhanced 3- to 5-fold, respectively, compared to levels found in normal ZL rats. However, the administration of KIOM-79 delayed the development of diabetic cataracts and prevented LEC apoptosis (70%) through the inhibition of AGEs, NF-κB-activation and iNOS expression. These observations suggest that KIOM-79 is useful in inhibiting diabetic cataractogenesis and acts through an antiapoptotic mechanism to protect LECs from injury.
Figures
References
-
- Kyselova Z, Stefek M, Bauer V. Pharmacological prevention of diabetic cataract. Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications. 2004;18(2):129–140. - PubMed
-
- Ramana KV, Friedrich B, Bhatnagar A, Srivastava SK. Aldose reductase mediates cytotoxic signals of hyperglycemia and TNF-alpha in human lens epithelial cells. FASEB Journal. 2003;17(2):315–317. - PubMed
-
- Hightower KR, Reddan JR, McCready JP, Dziedzic DC. Lens epithelium: a primary target of UVB irradiation. Experimental Eye Research. 1994;59(5):557–564. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed N. Advanced glycation endproducts—role in pathology of diabetic complications. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2005;67(1):3–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

