Anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and heme oxygenase-1 inhibitory activities of ravan napas, a formulation of uighur traditional medicine, in a rat model of allergic asthma
- PMID: 20953388
- PMCID: PMC2952321
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/725926
Anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and heme oxygenase-1 inhibitory activities of ravan napas, a formulation of uighur traditional medicine, in a rat model of allergic asthma
Abstract
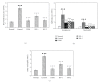
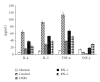
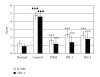
Ravan Napas (RN) is a traditional formula used to treat pulmonary symptoms and diseases such as coughing, breathing difficulty, and asthma in traditional Uighur medicine. The purpose of this study was to investigate the anti-inflammatory, and immuno-modulatory activity of RN in a well-characterized animal model of allergic asthma. Rats were sensitized with intraperitoneal (ip) ovalbumin (OVA) and alum, and then challenged with OVA aerosols. The asthma model rats were treated with RN; saline- and dexamethasone- (DXM-) treated rats served as normal and model controls. The bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) cellular differential and the concentrations of sICAM-1, IL-4, IL-5, TNF-α, INF-γ, and IgE in serum were measured. Lung sections underwent histological analysis. The immunohistochemistry S-P method was used to measure the expression of ICAM-1 and HO-1 in the lung. RN significantly reduced the number of inflammatory cells in BALF and lung tissues, decreased sICAM-1, IL-4, IL-5, TNF-α, and IgE in serum, and increased serum INF-γ. There was a marked suppression of ICAM-1 and HO-1 expression in the lung. Our results suggest that RN may have an anti-inflammatory and immuneregulatory effect on allergic bronchial asthma by modulating the balance between Th1/Th2 cytokines.
Figures



References
-
- Masoli M, Fabian D, Holt S, Beasley R. The global burden of asthma: executive summary of the GINA Dissemination Committee Report. Allergy. 2004;59(5):469–478. - PubMed
-
- Rees J, Price J. ABC of Asthma. 3rd edition. London, UK: BMJ; 1997. Asthma in children: prevalence and prospects for prevention; pp. 35–37.
-
- Barnes PJ. New aspects of asthma. Journal of Internal Medicine. 1992;231(5):453–461. - PubMed
-
- Rall TW. Drugs used for the treatment of asthma. In: Goodman-Gilman A, editor. The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 8th edition. Oxford, UK: McGraw-Hill; 1990. pp. 618–637.
-
- Brightling CE, Symon FA, Birring SS, Bradding P, Pavord ID, Wardlaw AJ. TH2 cytokine expression in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid T lymphocytes and bronchial submucosa is a feature of asthma and eosinophilic bronchitis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2002;110(6):899–905. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

