Evaluation of the Potential of Brazilian Propolis against UV-Induced Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 20953396
- PMCID: PMC2952332
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/863917
Evaluation of the Potential of Brazilian Propolis against UV-Induced Oxidative Stress
Abstract
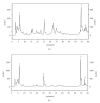
This study investigated the potential use of topically and orally administered propolis extracts to prevent UV irradiation-induced oxidative stress in skin. The results illustrated that green propolis extract (GPE) contained greater amounts of polyphenols, coumaric acid, drupanin, baccharin and artepillin C than did brown propolis extract (BPE). GPE showed higher antioxidant activity than BPE when the IC(50) (concentration that caused 50% inhibition) values were compared. Interesting, the oral treatment of hairless mice demonstrated a recovery of 30.0% for GPE and 22.8% for BPE with respect to UV irradiation-induced GSH depletion. The topical pretreatment of animals with both propolis extract solutions recovered around 14.0% of the depleted GSH. However, the employed treatments did not inhibit the increase of cutaneous proteinase secretion/activity caused by irradiation. These findings indicate that despite differences in composition and antioxidant properties, GPE and BPE both successfully prevent UV-induced GSH depletion in vivo and are both promising antioxidant systems against oxidative stress in skin. Based on these findings, complementary studies should be performed to enhance our understanding of the protective effects of propolis extracts in skin.
Figures
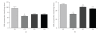
References
-
- Shindo Y, Witt E, Packer L. Antioxidant defense mechanisms in murine epidermis and dermis and their responses to ultraviolet light. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 1993;100(3):260–265. - PubMed
-
- Bonina F, Lanza M, Montenegro L, et al. Flavonoids as potential protective agents against photo-oxidative skin damage. International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 1996;145(1-2):87–94.
-
- Atoui AK, Mansouri A, Boskou G, Kefalas P. Tea and herbal infusions: their antioxidant activity and phenolic profile. Food Chemistry. 2005;89(1):27–36.
-
- Montenegro L, Bonina F, Rigano L, Giogilli S, Sirigu S. Protective effect evaluation of free radical scavengers on UVB induced human cutaneous erythema by skin reflectance spectrophotometry. International Journal of Cosmetic Science. 1995;17(3):91–103. - PubMed
-
- Díaz-Carballo D, Malak S, Bardenheuer W, Freistuehler M, Reusch HP. The contribution of plukenetione A to the anti-tumoral activity of Cuban propolis. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry. 2008;16(22):9635–9643. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

