Structures of 2-acetylaminofluorene modified DNA revisited: insight into conformational heterogeneity
- PMID: 20954689
- PMCID: PMC2981646
- DOI: 10.1021/tx100341u
Structures of 2-acetylaminofluorene modified DNA revisited: insight into conformational heterogeneity
Abstract
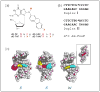
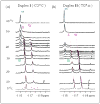
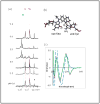
Despite the extensive data on dG-AAF, the major DNA adduct derived from the model carcinogen 2-acetylaminofluorene, little is known with respect to its solution structures. Here, we provide NMR/CD evidence for three conformers of dG-AAF in duplex DNA: major groove B-type (B), base-displaced stacked (S), and minor groove wedge (W). The S/B/W-conformational heterogeneities were found to be sensitive to the nature of the flanking DNA sequence contexts and pH.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Probing the conformational heterogeneity of the acetylaminofluorene-modified 2'-deoxyguanosine and DNA by 19F NMR spectroscopy.Biochemistry. 1999 Jun 8;38(23):7572-83. doi: 10.1021/bi990182d. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10360955
-
Solution conformation of [AF]dG opposite a -2 deletion site in a DNA duplex: intercalation of the covalently attached aminofluorene ring into the helix with base displacement of the C8-modified syn guanine and adjacent unpaired 3'-adenine into the major groove.Biochemistry. 1995 Dec 26;34(51):16641-53. doi: 10.1021/bi00051a012. Biochemistry. 1995. PMID: 8527437
-
Alternative conformations of DNA modified by N-2-acetylaminofluorene.J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;17(3):231-44. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.380170305. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981. PMID: 7328672
-
A molecular mechanics and dynamics study of the minor adduct between DNA and the carcinogen 2-(acetylamino)fluorene (dG-N2-AAF).Chem Res Toxicol. 1997 Oct;10(10):1123-32. doi: 10.1021/tx970092e. Chem Res Toxicol. 1997. PMID: 9348435
-
Dynamic conformational heterogeneities of carcinogen-DNA adducts and their mutagenic relevance.J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2004;22(2):57-90. doi: 10.1081/LESC-200038217. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2004. PMID: 16291518 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of base sequence context on the conformational heterogeneity of aristolactam-I adducted DNA: structural and energetic insights into sequence-dependent repair and mutagenicity.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015 Oct 23;5(1):197-209. doi: 10.1039/c5tx00302d. eCollection 2016 Jan 1. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2015. PMID: 30090337 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational insights into the lesion and sequence effects for arylamine-induced translesion DNA synthesis: 19F NMR, surface plasmon resonance, and primer kinetic studies.Biochemistry. 2014 Jun 24;53(24):4059-71. doi: 10.1021/bi5003212. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24915610 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational and thermodynamic properties modulate the nucleotide excision repair of 2-aminofluorene and 2-acetylaminofluorene dG adducts in the NarI sequence.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 May;40(9):3939-51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1307. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22241773 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive View of Translesion Synthesis in Escherichia coli.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2020 Jun 17;84(3):e00002-20. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00002-20. Print 2020 Aug 19. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32554755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conformational Insights into the Mechanism of Acetylaminofluorene-dG-Induced Frameshift Mutations in the NarI Mutational Hotspot.Chem Res Toxicol. 2016 Feb 15;29(2):213-26. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00484. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Chem Res Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26733364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neumann HG. Aromatic amines in experimental cancer research: tissue-specific effects, an old problem and new solutions. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2007;37:211–236. - PubMed
-
- Heflich RH, Neft RE. Genetic toxicity of 2-acetylaminofluorene, 2-aminofluorene and some of their metabolites and model metabolites. Mutation Research/Reviews in Genetic Toxicology. 1994;318:73–174. - PubMed
-
- Cui XS, Eriksson LC, Moller L. Formation and persistence of DNA adducts during and after a long-term administration of 2-nitrofluorene. Mutat Res. 1999;442:9–18. - PubMed
-
- Beland FA, Kadlubar FF. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. Spring-Verlag; Heidelberg: 1990. Metabolic activation and DNA adducts of aromatic amines and nitroaromatic hydocarbons; pp. 267–325.
-
- Shibutani S, Suzuki N, Tan X, Johnson F, Grollman AP. Influence of Flanking Sequence Context on the Mutagenicity of Acetylaminofluorene-Derived DNA Adducts in Mammalian Cells. Biochemistry. 2001;40:3717–3722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

