Hydrogen bonding between solutes in solvents octan-1-ol and water
- PMID: 20954704
- PMCID: PMC3034107
- DOI: 10.1021/jo1014646
Hydrogen bonding between solutes in solvents octan-1-ol and water
Abstract
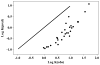
The 1:1 equilibrium constants, K, for the association of hydrogen bond bases and hydrogen bond acids have been determined by using octan-1-ol solvent at 298 K for 30 acid-base combinations. The values of K are much smaller than those found for aprotic, rather nonpolar solvents. It is shown that the log K values can satisfactorily be correlated against α(H)2·β(H)2, where α(H)2 and β(H)2 are the 1:1 hydrogen bond acidities and basicities of solutes. The slope of the plot, 2.938, is much smaller than those for log K values in the nonpolar organic solvents previously studied. An analysis of literature data on 1:1 hydrogen bonding in water yields a negative slope for a plot of log K against α(H)2·β(H)2, thus showing how the use of very strong hydrogen bond acids and bases does not lead to larger values of log K for 1:1 hydrogen bonding in water. It is suggested that for simple 1:1 association between monofunctional solutes in water, log K cannot be larger than about -0.1 log units. Descriptors have been obtained for the complex between 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol and propanone, and used to analyze solvent effects on the two reactants, the complex, and the complexation constant.
Figures
References
-
- Joesten MD, Schaad LJ. Hydrogen Bonding. Marcel Dekker; New York: 1974.
-
- Green RD. Hydrogen Bonding by C-H Groups. Macmillan; London: 1974.
-
- Abboud JL, Bellon L. Ann Chim. 1970;5:63–74.
-
- Abraham MH, Duce PP, Grellier PL, Prior DV, Morris JJ, Taylor PJ. Terahedron Lett. 1988;29:1587–1590.
-
- Abraham MH, Grellier PL, Prior DV, Duce PP, Morris JJ, Taylor PJ. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans. 1989;2:699–711.