Empyema thoracis: new insights into an old disease
- PMID: 20956197
- PMCID: PMC9487281
- DOI: 10.1183/09059180.00005610
Empyema thoracis: new insights into an old disease
Abstract
Pleural infection is a disease of historical importance and is still a modern menace, with incidences rising in adults and children, and a significant mortality in adults. Basic research is hampered by limitations with in vivo models, and the bacteriology of empyema is complex. The role of thoracic ultrasound in guiding investigation and drainage of empyema is clear. Prompt treatment with appropriate systemic antibiotics and chest tube drainage are the key; in cases of failure of these measures, thoracic surgery is of proven efficacy in the treatment of this age-old disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.C.G. Lee is a co-investigator of the British Thoracic Society Multicentre Intrapleural Sepsis Trial 2, which is partly funded by Roche Ltd.
Figures
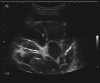
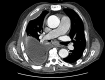
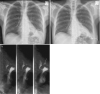
References
-
- Dunham EK, Graham EA, Mitchell JF, et al. , Empyema commission. Cases of empyema at Camp Lee, VA. Preliminary report. Am J Med Assoc 1918; 71: 366–373.
-
- Davies CW, Kearney SE, Gleeson FV, et al. . Predictors of outcome and long-term survival in patients with pleural infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 160: 1682–1687. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson AD, Prescott RJ, Selkon JB, et al. . The clinical course and management of thoracic empyema. QJM 1996; 89: 285–289. - PubMed
-
- Maskell NA, Davies CW, Nunn AJ, et al. . UK controlled trial of intrapleural streptokinase for pleural infection. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 865–874. - PubMed
-
- Desai G, Amadi W. Three years' experience of empyema thoracis in association with HIV infection. Trop Doct 2001; 31: 106–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
