Costs and consequences of universal sibling screening for vesicoureteral reflux: decision analysis
- PMID: 20956427
- PMCID: PMC3098562
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2010-0744
Costs and consequences of universal sibling screening for vesicoureteral reflux: decision analysis
Abstract
Objective: Our objective was to evaluate screening for vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) among siblings of patients with VUR, in terms of cost, radiation exposure, and number of febrile urinary tract infections (fUTIs) averted.
Methods: We constructed a Markov model to evaluate 2 competing management options, that is, universal screening (cystographic evaluation of all siblings without symptoms) and usual care (cystographic evaluation of siblings only after fUTIs). Published data were used to inform all model inputs. Costs were estimated by using a societal perspective.
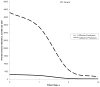
Results: Universal screening yielded 2980 fUTIs, whereas usual care yielded 6330. Therefore, universal screening for VUR in a cohort of 100,000 siblings 1 year of age without symptoms resulted in the prevention of 1 initial fUTI per 3360 siblings, at an excess cost of $55,600 per averted fUTI, in comparison with usual care. These estimates were heavily dependent on screening age and the effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis; prevention of a single fUTI would require screening of 166 siblings 5 years of age and 694 siblings 10 years of age. Similarly, if prophylaxis was ineffective in preventing fUTIs, then up to 10,000 siblings would need to be screened for prevention of a single fUTI.
Conclusions: Prevention of a single fUTI would require screening of 30 to 430 siblings 1 year of age without symptoms, at an estimated excess cost of $56,000 to $820,000 per averted fUTI. These estimates are heavily dependent on screening age and the effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retrospective Analysis to Determine the Optimal Timing to Discontinue Continuous Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Patients with Primary Vesicoureteral Reflux.Urol Int. 2019;102(4):462-467. doi: 10.1159/000497312. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Urol Int. 2019. PMID: 30917379
-
Computer model predicting breakthrough febrile urinary tract infection in children with primary vesicoureteral reflux.J Pediatr Urol. 2016 Oct;12(5):288.e1-288.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 31. J Pediatr Urol. 2016. PMID: 27072485
-
Incidence of Urinary Tract Infection Among Siblings of Children With Vesicoureteral Reflux.Acad Pediatr. 2016 Jul;16(5):489-495. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Nov 14. Acad Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 26589543 Free PMC article.
-
Screening siblings for vesicoureteral reflux.J Urol. 2002 Nov;168(5):2138-41. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64337-6. J Urol. 2002. PMID: 12394743 Review.
-
EAU guidelines on vesicoureteral reflux in children.Eur Urol. 2012 Sep;62(3):534-42. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.05.059. Epub 2012 Jun 5. Eur Urol. 2012. PMID: 22698573 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiology and Clinical Research Design, Part 2: Principles.Neoreviews. 2015;16(2):e94-e108. doi: 10.1542/neo.16-2-e94. Neoreviews. 2015. PMID: 26236171 Free PMC article.
-
Health services research in urology.World J Urol. 2011 Jun;29(3):273-6. doi: 10.1007/s00345-011-0657-4. Epub 2011 Feb 27. World J Urol. 2011. PMID: 21359548 Review.
References
-
- Skoog SJ, Peters CA, Arant BS, et al. Pediatric Vesicoureteral Reflux Guidelines Panel summary report: clinical practice guidelines for screening siblings of children with vesicoureteral reflux and neonates/infants with prenatal hydronephrosis. J Urol. 2010;184(3):1145–1151. - PubMed
-
- Ferrer FA, McKenna PH, Hochman HI, Herndon A. Results of a vesicoureteral reflux practice pattern survey among American Academy of Pediatrics, Sectionon Pediatric Urology members. J Urol. 1998;160(3):1031–1037. - PubMed
-
- Bonnin F, Lottmann H, Sauty L, et al. Scintigraphic screening for renal damage in siblings of children with symptomatic primary vesicoureteric reflux. BJU Int. 2001;87(6):463–466. - PubMed
-
- Connolly LP, Treves ST, Zurakowski D, Bauer SB. Natural history of vesicoureteral reflux in siblings. J Urol. 1996;156(5):1805–1807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources