Sphingolipid-mediated inhibition of apoptotic cell clearance by alveolar macrophages
- PMID: 20956540
- PMCID: PMC3001012
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.137604
Sphingolipid-mediated inhibition of apoptotic cell clearance by alveolar macrophages
Abstract
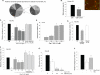
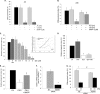
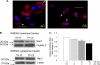
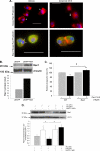
A decreased clearance of apoptotic cells (efferocytosis) by alveolar macrophages (AM) may contribute to inflammation in emphysema. The up-regulation of ceramides in response to cigarette smoking (CS) has been linked to AM accumulation and increased detection of apoptotic alveolar epithelial and endothelial cells in lung parenchyma. We hypothesized that ceramides inhibit the AM phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Release of endogenous ceramides via sphingomyelinase or exogenous ceramide treatments dose-dependently impaired apoptotic Jurkat cell phagocytosis by primary rat or human AM, irrespective of the molecular species of ceramide. Similarly, in vivo augmentation of lung ceramides via intratracheal instillation in rats significantly decreased the engulfment of instilled target apoptotic thymocytes by resident AM. The mechanism of ceramide-induced efferocytosis impairment was dependent on generation of sphingosine via ceramidase. Sphingosine treatment recapitulated the effects of ceramide, dose-dependently inhibiting apoptotic cell clearance. The effect of ceramide on efferocytosis was associated with decreased membrane ruffle formation and attenuated Rac1 plasma membrane recruitment. Constitutively active Rac1 overexpression rescued AM efferocytosis against the effects of ceramide. CS exposure significantly increased AM ceramides and recapitulated the effect of ceramides on Rac1 membrane recruitment in a sphingosine-dependent manner. Importantly, CS profoundly inhibited AM efferocytosis via ceramide-dependent sphingosine production. These results suggest that excessive lung ceramides may amplify lung injury in emphysema by causing both apoptosis of structural cells and inhibition of their clearance by AM.
Figures
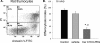
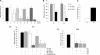
References
-
- Yoshida T., Tuder R. M. (2007) Physiol. Rev. 87, 1047–1082 - PubMed
-
- Tuder R. M., Petrache I., Elias J. A., Voelkel N. F., Henson P. M. (2003) Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 28, 551–554 - PubMed
-
- Tuder R. M., Zhen L., Cho C. Y., Taraseviciene-Stewart L., Kasahara Y., Salvemini D., Voelkel N. F., Flores S. C. (2003) Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 29, 88–97 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

