Targeted inactivation of Mapk4 in mice reveals specific nonredundant functions of Erk3/Erk4 subfamily mitogen-activated protein kinases
- PMID: 20956558
- PMCID: PMC3004264
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01147-10
Targeted inactivation of Mapk4 in mice reveals specific nonredundant functions of Erk3/Erk4 subfamily mitogen-activated protein kinases
Abstract
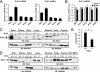
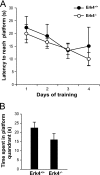
Erk4 and Erk3 are atypical members of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase family. The high sequence identity of Erk4 and Erk3 proteins and the similar organization of their genes imply that the two protein kinases are paralogs. Recently, we have shown that Erk3 function is essential for neonatal survival and critical for the establishment of fetal growth potential and pulmonary function. To investigate the specific functions of Erk4, we have generated mice with a targeted disruption of the Mapk4 gene. We show that Erk4-deficient mice are viable and fertile and exhibit no gross morphological or physiological anomalies. Loss of Erk4 is not compensated by changes in Erk3 expression or activity during embryogenesis or in adult tissues. We further demonstrate that additional loss of Erk4 does not exacerbate the fetal growth restriction and pulmonary immaturity phenotypes of Erk3(-/-) mice and does not compromise the viability of Erk3(+/-) neonates. Interestingly, behavioral phenotyping revealed that Erk4-deficient mice manifest depression-like behavior in the forced-swimming test. Our analysis indicates that the MAP kinase Erk4 is dispensable for mouse embryonic development and reveals that Erk3 and Erk4 have acquired specialized functions through evolutionary diversification.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Germ Line Deletion Reveals a Nonessential Role of Atypical Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 6/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 3.Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Mar 1;39(6):e00516-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00516-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30642948 Free PMC article.
-
Activation loop phosphorylation of ERK3/ERK4 by group I p21-activated kinases (PAKs) defines a novel PAK-ERK3/4-MAPK-activated protein kinase 5 signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 25;286(8):6470-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.181529. Epub 2010 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21177870 Free PMC article.
-
Activation loop phosphorylation of the atypical MAP kinases ERK3 and ERK4 is required for binding, activation and cytoplasmic relocalization of MK5.J Cell Physiol. 2008 Dec;217(3):778-88. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21560. J Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18720373
-
MK5: A novel regulator of cardiac fibroblast function?IUBMB Life. 2017 Oct;69(10):785-794. doi: 10.1002/iub.1677. Epub 2017 Sep 11. IUBMB Life. 2017. PMID: 28941148 Review.
-
Atypical MAPKs in cancer.FEBS J. 2025 May;292(9):2173-2188. doi: 10.1111/febs.17283. Epub 2024 Sep 30. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 39348153 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
On the Therapeutic Potential of ERK4 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 21;15(1):25. doi: 10.3390/cancers15010025. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36612022 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological roles of mitogen-activated-protein-kinase-activated p38-regulated/activated protein kinase.World J Biol Chem. 2011 May 26;2(5):73-89. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v2.i5.73. World J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21666810 Free PMC article.
-
Deubiquitinating Enzyme USP20 Regulates Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 3 Stability and Biological Activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Apr 14;37(9):e00432-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00432-16. Print 2017 May 1. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28167606 Free PMC article.
-
Germ Line Deletion Reveals a Nonessential Role of Atypical Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 6/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 3.Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Mar 1;39(6):e00516-18. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00516-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30642948 Free PMC article.
-
The catalytic activity of the mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular signal-regulated kinase 3 is required to sustain CD4+ CD8+ thymocyte survival.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Sep 15;34(18):3374-87. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01701-13. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25002529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aberg, E., M. Perander, B. Johansen, C. Julien, S. Meloche, S. M. Keyse, and O. M. Seternes. 2006. Regulation of MAPK-activated protein kinase 5 activity and subcellular localization by the atypical MAPK ERK4/MAPK4. J. Biol. Chem. 281:35499-35510. - PubMed
-
- Braun, T., M. A. Rudnicki, H. H. Arnold, and R. Jaenisch. 1992. Targeted inactivation of the muscle regulatory gene Myf-5 results in abnormal rib development and perinatal death. Cell 71:369-382. - PubMed
-
- Cameron, H. A., and R. McKay. 1998. Stem cells and neurogenesis in the adult brain. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 8:677-680. - PubMed
-
- Coulombe, P., and S. Meloche. 2007. Atypical mitogen-activated protein kinases: structure, regulation and functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1773:1376-1387. - PubMed
-
- Coulombe, P., G. Rodier, S. Pelletier, J. Pellerin, and S. Meloche. 2003. Rapid turnover of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 3 by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway defines a novel paradigm of mitogen-activated protein kinase regulation during cellular differentiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23:4542-4558. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
