Anti-Inflammatory benefits of antibiotic-induced neutrophil apoptosis: tulathromycin induces caspase-3-dependent neutrophil programmed cell death and inhibits NF-kappaB signaling and CXCL8 transcription
- PMID: 20956586
- PMCID: PMC3019645
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01052-10
Anti-Inflammatory benefits of antibiotic-induced neutrophil apoptosis: tulathromycin induces caspase-3-dependent neutrophil programmed cell death and inhibits NF-kappaB signaling and CXCL8 transcription
Abstract
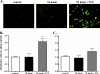
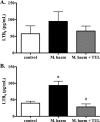
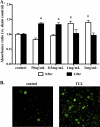
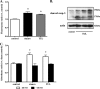
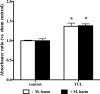
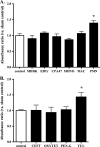
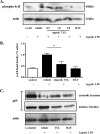
Clearance of apoptotic neutrophils is a central feature of the resolution of inflammation. Findings indicate that immuno-modulation and induction of neutrophil apoptosis by macrolide antibiotics generate anti-inflammatory benefits via mechanisms that remain obscure. Tulathromycin (TUL), a new antimicrobial agent for bovine respiratory disease, offers superior clinical efficacy for reasons not fully understood. The aim of this study was to identify the immuno-modulating effects of tulathromycin and, in this process, to establish tulathromycin as a new model for characterizing the novel anti-inflammatory properties of antibiotics. Bronchoalveolar lavage specimens were collected from Holstein calves 3 and 24 h postinfection, challenged intratracheally with live Mannheimia haemolytica (2 × 10(7) CFU), and treated with vehicle or tulathromycin (2.5 mg/kg body weight). Terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) revealed that tulathromycin treatment significantly increased leukocyte apoptosis and reduced levels of proinflammatory leukotriene B(4) in M. haemolytica-challenged calves. In vitro, tulathromycin concentration dependently induced apoptosis in freshly isolated bovine neutrophils from healthy steers in a capase-3-dependent manner but failed to induce apoptosis in bovine fibroblasts, epithelial cells, and endothelial cells, as well as freshly isolated bovine blood monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. The proapoptotic effects of TUL were also, in part, drug specific; equimolar concentrations of penicillin G, oxytetracycline, and ceftiofur failed to cause apoptosis in bovine neutrophils. In addition, tulathromycin significantly reduced levels of phosphorylated IκBα, nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65, and mRNA levels of proinflammatory interleukin-8 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated bovine neutrophils. The findings illustrate novel mechanisms through which tulathromycin confers anti-inflammatory benefits.
Figures
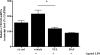
References
-
- Akgul, C., D. A. Moulding, and S. W. Edwards. 2001. Molecular control of neutrophil apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 487:318-322. - PubMed
-
- Barkett, M., D. Xue, H. R. Horvitz, and T. D. Gilmore. 1997. Phosphorylation of IkappaB-alpha inhibits its cleavage by caspase CPP32 in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 272:29419-29422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

