Differential effects of paromomycin on ribosomes of Leishmania mexicana and mammalian cells
- PMID: 20956601
- PMCID: PMC3019668
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00506-10
Differential effects of paromomycin on ribosomes of Leishmania mexicana and mammalian cells
Abstract
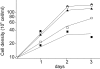
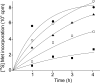
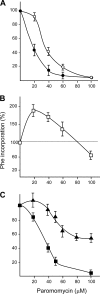
Paromomycin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic having low mammalian cell toxicity, is one of the drugs currently used in the chemotherapy of cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis. In order to understand the mode of action of this antibiotic at the molecular level, we have investigated the effects of paromomycin on protein synthesis in Leishmania and its mammalian hosts. We were able to demonstrate that in vivo protein synthesis in the promastigote stage of the parasite and its proliferation rate are markedly inhibited by paromomycin while being only slightly affected by other aminoglycoside antibiotics, such as streptomycin and neomycin B. Furthermore, both in vitro polypeptide synthesis induced by poly(U) as mRNA and accuracy of translation are significantly decreased by paromomycin in cell-free systems containing ribosomal particles of Leishmania promastigotes. Conversely, when ribosomes from mammalian cells are used instead of the protozoan particles, polyphenylalanine synthesis is only barely reduced by the antibiotic and the translation misreading remains almost unaltered. Surface plasmon resonance analysis of the interaction between paromomycin and protozoan or mammalian cell ribosomal RNAs shows a strong binding of antibiotic to the parasite ribosomal decoding site and practically no interaction with the mammalian cell counterpart. Our results indicating differential effects of paromomycin on the translation processes of the Leishmania parasite and its mammalian hosts can explain the therapeutic efficiency of this antibiotic as an antileishmaniasis agent.
Figures


References
-
- Algranati, I. D. 1980. Inhibition of polypeptide synthesis initiation by a change of Mg2+ concentration in wheat germ cell-free systems. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 96:54-60. - PubMed
-
- Bashan, A., and A. Yonath. 2008. Correlating ribosome function with high-resolution structures. Trends. Microbiol. 16:326-335. - PubMed
-
- Basselin, M., M. A. Badet-Denisot, F. Lawrence, and M. Robert-Gero. 1997. Effects of pentamidine on polyamine level and biosynthesis in wild-type, pentamidine-treated, and pentamidine-resistant Leishmania. Exp. Parasitol. 85:274-282. - PubMed
-
- Beakier-Gingras, L., and P. Phoenix. 1984. The control of accuracy during protein synthesis in Escherichia coli and perturbations of this control by streptomycin, neomycin or ribosomal mutations. Can. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 62:231-244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

