Imaging for the diagnosis and management of ductal carcinoma in situ
- PMID: 20956833
- PMCID: PMC5161079
- DOI: 10.1093/jncimonographs/lgq037
Imaging for the diagnosis and management of ductal carcinoma in situ
Abstract
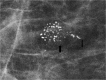
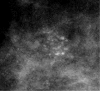
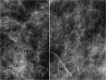
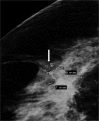
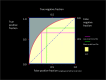
Diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) has increased dramatically in parallel with the increased use of screening mammography. There are specific mammographic findings, most associated with shapes (amorphous, fine and coarse pleomorphic, and fine linear) and distributions (linear and segmental) of calcifications that permit a reasonable sensitivity for detection of DCIS without an unreasonable decrease in specificity, especially in view of the dramatic decrease in breast cancer mortality associated with early detection. While some DCIS may never progress to invasive disease, at this time, we cannot make that separation. This should be an active area for research.
Figures



References
-
- Blichert-Toft M, Graversen HP, Andersen J, et al. In sity breast carcinomas: a population-based study on frequency, growth pattern, and clinical aspects. World J Surg. 1988;12:845–851. - PubMed
-
- Ward BA, McKhann CF, Ravikumar TS. Ten-year follow-up of breast carcinoma in situ in Connecticut. Arch Surg. 1992;127(12):1392–1395. - PubMed
-
- Barreau B, deMascarel I, Feuga C, et al. Mammography of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: review of 909 cases with radiographic-pathologic correlation. Eur J Radiol. 2005;54(1):55–61. - PubMed
-
- Tabar L, Duffy SW, Burhenne LW, et al. New Swedish breast cancer detection results for women aged 40-49. Cancer. 1993;72(4 suppl):1437–1448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

