Electrophysiological effects of SKF83959 on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons: potential mechanisms for the drug's neuroprotective effects
- PMID: 20957037
- PMCID: PMC2948503
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013118
Electrophysiological effects of SKF83959 on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons: potential mechanisms for the drug's neuroprotective effects
Abstract
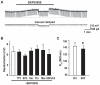
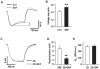
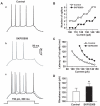
Although the potent anti-parkinsonian action of the atypical D₁-like receptor agonist SKF83959 has been attributed to the selective activation of phosphoinositol(PI)-linked D₁ receptor, whereas the mechanism underlying its potent neuroprotective effect is not fully understood. In the present study, the actions of SKF83959 on neuronal membrane potential and neuronal excitability were investigated in CA1 pyramidal neurons of rat hippocampal slices. SKF83959 (10-100 µM) caused a concentration-dependent depolarization, associated with a reduction of input resistance in CA1 pyramidal neurons. The depolarization was blocked neither by antagonists for D₁, D₂, 5-HT(2A/2C) receptors and α₁-adrenoceptor, nor by intracellular dialysis of GDP-β-S. However, the specific HCN channel blocker ZD7288 (10 µM) antagonized both the depolarization and reduction of input resistance caused by SKF83959. In voltage-clamp experiments, SKF83959 (10-100 µM) caused a concentration-dependent increase of Ih current in CA1 pyramidal neurons, which was independent of D₁ receptor activation. Moreover, SKF83959 (50 µM) caused a 6 mV positive shift in the activation curve of Ih and significantly accelerated the activation of Ih current. In addition, SKF83959 also reduced the neuronal excitability of CA1 pyramidal neurons, which was manifested by the decrease in the number and amplitude of action potentials evoked by depolarizing currents, and by the increase of firing threshold and rhoebase current. The above results suggest that SKF83959 increased Ih current through a D₁ receptor-independent mechanism, which led to the depolarization of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. These findings provide a novel mechanism for the drug's neuroprotective effects, which may contributes to its therapeutic benefits in Parkinson's disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of SKF83959 on the excitability of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons: a modeling study.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 Jun;35(6):738-51. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.23. Epub 2014 May 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 24858313 Free PMC article.
-
SKF83959 suppresses excitatory synaptic transmission in rat hippocampus via a dopamine receptor-independent mechanism.J Neurosci Res. 2011 Aug;89(8):1259-66. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22653. Epub 2011 May 2. J Neurosci Res. 2011. PMID: 21538463
-
Neuroprotective effects of atypical D1 receptor agonist SKF83959 are mediated via D1 receptor-dependent inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and a receptor-independent anti-oxidative action.J Neurochem. 2008 Feb;104(4):946-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05062.x. Epub 2007 Nov 14. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18005341
-
Arylbenzazepines are potent modulators for the delayed rectifier K+ channel: a potential mechanism for their neuroprotective effects.PLoS One. 2009 Jun 5;4(6):e5811. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005811. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19503734 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of phosphatidylinositol-linked D1-like receptors increases spontaneous glutamate release in rat somatosensory cortical neurons in vitro.Brain Res. 2010 Jul 9;1343:20-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.04.043. Epub 2010 Apr 24. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20420815
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in the Realm of Allosteric Modulators for Opioid Receptors for Future Therapeutics.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2017 Jun 21;8(6):1147-1158. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00090. Epub 2017 Apr 7. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28368571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of SKF83959 on the excitability of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons: a modeling study.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 Jun;35(6):738-51. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.23. Epub 2014 May 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 24858313 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological properties of embryonic stem cell-derived neurons.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e24169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024169. Epub 2011 Aug 26. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21887381 Free PMC article.
-
Acutely elevated O-GlcNAcylation suppresses hippocampal activity by modulating both intrinsic and synaptic excitability factors.Sci Rep. 2019 May 13;9(1):7287. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43017-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31086206 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric Modulation of Sigma-1 Receptors Elicits Rapid Antidepressant Activity.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016 May;22(5):368-77. doi: 10.1111/cns.12502. Epub 2016 Feb 8. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016. PMID: 26854125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jin LQ, Goswami S, Cai G, Zhen X, Friedman E. SKF83959 selectively regulates phosphatidylinositol-linked D1 dopamine receptors in rat brain. J Neurochem. 2003;85:378–386. - PubMed
-
- Panchalingam S, Undie AS. SKF83959 exhibits biochemical agonism by stimulating [35S]GTP-γ-S binding and phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat and monkey brain. Neuropharmacology. 2001;40:826–837. - PubMed
-
- Arnt J, Hyttel J, Sanchez C. Partial and full dopamine D1 receptor agonists in mice and rats: relation between behavioural effects and stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992;213:259–267. - PubMed
-
- Cools AR, Lubbers L, van Oosten RV, Andringa G. SKF 83959 is an antagonist of dopamine D1-like receptors in the prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens: a key to its antiparkinsonian effect in animals? Neuropharmacology. 2002;42:237–245. - PubMed
-
- Neumeyer JL, Kula NS, Bergman J, Baldessarini RJ. Receptor affinities of dopamine D1 receptor-selective novel phenylbenzazepines. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;474:137–140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

