Drug off-target effects predicted using structural analysis in the context of a metabolic network model
- PMID: 20957118
- PMCID: PMC2950675
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000938
Drug off-target effects predicted using structural analysis in the context of a metabolic network model
Abstract
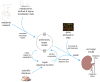
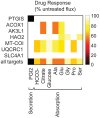
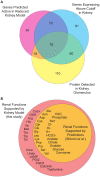
Recent advances in structural bioinformatics have enabled the prediction of protein-drug off-targets based on their ligand binding sites. Concurrent developments in systems biology allow for prediction of the functional effects of system perturbations using large-scale network models. Integration of these two capabilities provides a framework for evaluating metabolic drug response phenotypes in silico. This combined approach was applied to investigate the hypertensive side effect of the cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitor torcetrapib in the context of human renal function. A metabolic kidney model was generated in which to simulate drug treatment. Causal drug off-targets were predicted that have previously been observed to impact renal function in gene-deficient patients and may play a role in the adverse side effects observed in clinical trials. Genetic risk factors for drug treatment were also predicted that correspond to both characterized and unknown renal metabolic disorders as well as cryptic genetic deficiencies that are not expected to exhibit a renal disorder phenotype except under drug treatment. This study represents a novel integration of structural and systems biology and a first step towards computational systems medicine. The methodology introduced herein has important implications for drug development and personalized medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
A patent application has been filed for the modeling and simulation approach used in this study for predicting drug responses, metabolic disorders, and risk factors for treatment.
Figures



References
-
- Hellerstein MK. Exploiting complexity and the robustness of network architecture for drug discovery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;325:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Searls DB. Data integration: challenges for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:45–58. - PubMed
-
- Paolini GV, Shapland RH, van Hoorn WP, Mason JS, Hopkins AL. Global mapping of pharmacological space. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:805–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

