An integrated micro- and macroarchitectural analysis of the Drosophila brain by computer-assisted serial section electron microscopy
- PMID: 20957184
- PMCID: PMC2950124
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000502
An integrated micro- and macroarchitectural analysis of the Drosophila brain by computer-assisted serial section electron microscopy
Abstract
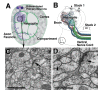
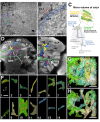
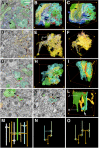
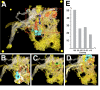
The analysis of microcircuitry (the connectivity at the level of individual neuronal processes and synapses), which is indispensable for our understanding of brain function, is based on serial transmission electron microscopy (TEM) or one of its modern variants. Due to technical limitations, most previous studies that used serial TEM recorded relatively small stacks of individual neurons. As a result, our knowledge of microcircuitry in any nervous system is very limited. We applied the software package TrakEM2 to reconstruct neuronal microcircuitry from TEM sections of a small brain, the early larval brain of Drosophila melanogaster. TrakEM2 enables us to embed the analysis of the TEM image volumes at the microcircuit level into a light microscopically derived neuro-anatomical framework, by registering confocal stacks containing sparsely labeled neural structures with the TEM image volume. We imaged two sets of serial TEM sections of the Drosophila first instar larval brain neuropile and one ventral nerve cord segment, and here report our first results pertaining to Drosophila brain microcircuitry. Terminal neurites fall into a small number of generic classes termed globular, varicose, axiform, and dendritiform. Globular and varicose neurites have large diameter segments that carry almost exclusively presynaptic sites. Dendritiform neurites are thin, highly branched processes that are almost exclusively postsynaptic. Due to the high branching density of dendritiform fibers and the fact that synapses are polyadic, neurites are highly interconnected even within small neuropile volumes. We describe the network motifs most frequently encountered in the Drosophila neuropile. Our study introduces an approach towards a comprehensive anatomical reconstruction of neuronal microcircuitry and delivers microcircuitry comparisons between vertebrate and insect neuropile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Hartenstein V, Spindler S, Pereanu W, Fung S. The development of the Drosophila larval brain. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;628:1–31. - PubMed
-
- Hartenstein V, Cardona A, Pereanu W, Younossi-Hartenstein A. Modeling the developing Drosophila brain: rationale, technique and application. BioScience. 2008;58:823–836.
-
- Cropley V. L, Fujita M, Innis R. B, Nathan P. J. Molecular imaging of the dopaminergic system and its association with human cognitive function. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;59:898–907. - PubMed
-
- May A. Neuroimaging: visualising the brain in pain. Neurol Sci. 2007;28(Suppl 2):S101–S107. - PubMed
-
- Shibasaki H. Human brain mapping: hemodynamic response and electrophysiology. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008;119:731–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

