Clinical and functional evaluation of patients with rectocele and mucosal prolapse treated with transanal repair of rectocele and rectal mucosectomy with a single circular stapler (TRREMS)
- PMID: 20957403
- PMCID: PMC2988992
- DOI: 10.1007/s10151-010-0649-1
Clinical and functional evaluation of patients with rectocele and mucosal prolapse treated with transanal repair of rectocele and rectal mucosectomy with a single circular stapler (TRREMS)
Abstract
Background: The aim of the present study was to make a preoperative and postoperative clinical and functional evaluation of patients who underwent transanal repair of rectocele and rectal mucosectomy with a single circular stapler (TRREMS procedure) as treatment for obstructed defecation syndrome (ODS) caused by rectocele and rectal mucosal prolapse (RMP).
Methods: This prospective study included 35 female patients, 34 multiparous and one nulliparous, with an average age of 47.5 years (range 31-67 years), rectocele grade II (n = 13/37.1%) or grade III (n = 22/62.9%), associated with RMP. The study parameters included ODS, constipation, functional continence scores and pre- and postoperative cinedefecographic findings.
Results: The average preoperative ODS score, the constipation score and the functional continence score were significantly reduced after surgery from 10.63 to 2.91 (p = 0.001), 15.23 to 4.46 (p = 0.001) and 2.77 to 1.71 (p = 0.001), respectively. Between the first and the eighth postoperative day, the average visual analog scale pain score fell from 5.23 to 1.20 (p = 0.001). Satisfaction with treatment outcome was 79.97, 86.54, 87.65 and 88.06 at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months, respectively. Cinedefecography revealed average reductions in rectocele size from 19.23 ± 8.84 mm (3-42) to 6.68 ± 3.65 mm (range 0-7) at rest and from 34.89 ± 12.30 mm (range 20-70) to 10.94 ± 5.97 mm (range 0-25) during evacuation (both P = 0.001).
Conclusion: The TRREMS procedure is a safe and efficient technique associated with satisfactory anatomic and functional results and with a low incidence of postoperative pain and complications.
Figures

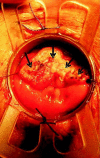
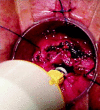
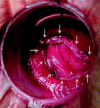
Comment in
-
The role of hemorrhoidectomy in rectocele complicated by grade 3-4 hemorrhoids.Tech Coloproctol. 2013 Apr;17(2):249. doi: 10.1007/s10151-012-0889-3. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Tech Coloproctol. 2013. PMID: 22956208 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pescatori M, Favetta U, Dedola S, Orsini S. Transanal stapled excision of rectal mucosal prolapse. Tech Coloproctol. 1997;1:96–98.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

