The constitutive activation of Jak2-V617F is mediated by a π stacking mechanism involving phenylalanines 595 and 617
- PMID: 20958061
- PMCID: PMC2982877
- DOI: 10.1021/bi1014858
The constitutive activation of Jak2-V617F is mediated by a π stacking mechanism involving phenylalanines 595 and 617
Abstract
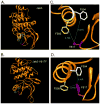
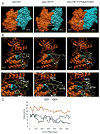
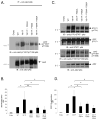
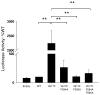
Somatic mutations in the Jak2 allele that lead to constitutive kinase activation of the protein have been identified in human disease conditions such as the myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs). The most common mutation in these patients is a V617F substitution mutation, which is believed to play a causative role in the MPN pathogenesis. As such, identifying the molecular basis for the constitutive activation of Jak2-V617F is important for understanding its clinical implications and potential treatment. Here, we hypothesized that conversion of residue 617 from Val to Phe resulted in the formation of novel π stacking interactions with neighboring Phe residues. To test this, we first examined the Jak2 structure via molecular modeling and identified a potential π stacking interaction between F594, F595, and F617. Disruption of this interaction through site-directed mutagenesis impaired Jak2 autophosphorylation, Jak2-dependent gene transcription, and in vitro kinase activity of the Jak2-V617F protein. Further, substitution of F594 and F595 with Trp did not affect Jak2 function significantly, but replacement with charged residues did, showing the importance of aromaticity and hydropathy index conservation at these positions. Using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, we found that the π stacking interaction between residues 595 and 617 in the Jak2-V617F protein was of much greater energy and conformed to the properties of π stacking, relative to the Jak2-WT or Jak2-V617F/F594A/F595A. In summary, we have identified a π stacking interaction between F595 and F617 that is specific to and is critical for the constitutive activation of Jak2-V617F.
Figures


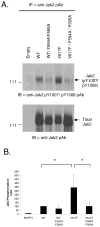
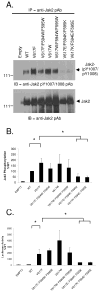
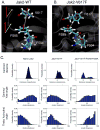
References
-
- Neubauer H, Cumano A, Muller M, Wu H, Huffstadt U, Pfeffer K. Jak2 deficiency defines an essential developmental checkpoint in definitive hematopoiesis. Cell. 1998;93:397–409. - PubMed
-
- Parganas E, Wang D, Stravopodis D, Topham DJ, Marine JC, Teglund S, Vanin EF, Bodner S, Colamonici OR, van Deursen JM, Grosveld G, Ihle JN. Jak2 is essential for signaling through a variety of cytokine receptors. Cell. 1998;93:385–395. - PubMed
-
- Sandberg EM, Wallace TA, Godeny MD, VonDerLinden D, Sayeski PP. Jak2 tyrosine kinase: a true jak of all trades? Cell Biochem Biophys. 2004;41:207–232. - PubMed
-
- Witthuhn BA, Quelle FW, Silvennoinen O, Yi T, Tang B, Miura O, Ihle JN. JAK2 associates with the erythropoietin receptor and is tyrosine phosphorylated and activated following stimulation with erythropoietin. Cell. 1993;74:227–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

