Phosphate toxicity: new insights into an old problem
- PMID: 20958267
- PMCID: PMC3120105
- DOI: 10.1042/CS20100377
Phosphate toxicity: new insights into an old problem
Abstract
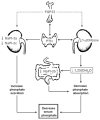
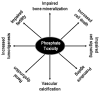
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient required for critical biological reactions that maintain the normal homoeostatic control of the cell. This element is an important component of different cellular structures, including nucleic acids and cell membranes. Adequate phosphorus balance is vital for maintaining basic cellular functions, ranging from energy metabolism to cell signalling. In addition, many intracellular pathways utilize phosphate ions for important cellular reactions; therefore, homoeostatic control of phosphate is one of the most delicate biological regulations. Impaired phosphorus balance can affect the functionality of almost every human system, including musculoskeletal and cardiovascular systems, ultimately leading to an increase in morbidity and mortality of the affected patients. Human and experimental studies have found that delicate balance among circulating factors, like vitamin D, PTH (parathyroid hormone) and FGF23 (fibroblast growth factor 23), are essential for regulation of physiological phosphate balance. Dysregulation of these factors, either alone or in combination, can induce phosphorus imbalance. Recent studies have shown that suppression of the FGF23-klotho system can lead to hyperphosphataemia with extensive tissue damage caused by phosphate toxicity. The cause and consequences of phosphate toxicity will be briefly summarized in the present review.
Figures
References
-
- Fukagawa M, Hamada Y, Nakanishi S, Tanaka M. The kidney and bone metabolism: nephrologists’ point of view. J Bone Miner Metab. 2006;24:434–438. - PubMed
-
- Laroche M, Boyer JF. Phosphate diabetes, tubular phosphate reabsorption and phosphatonins. J Bone Spine. 2005;72:376–381. - PubMed
-
- Huttunen MM, Pietila PE, Viljakainen HT, Lamberg-Allardt CJ. Prolonged increase in dietary phosphate intake alters bone mineralization in adult male rats. J Nutr Biochem. 2006;17:479–484. - PubMed
-
- Heilberg IP, Weisinger JR. Bone disease in idiopathic hypercalciuria. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2006;15:394–402. - PubMed
-
- Gaasbeek A, Meinders AE. Hypophosphatemia: an update on its etiology and treatment. Am J Med. 2005;118:1094–1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

