MicroRNAs in skin and wound healing
- PMID: 20959495
- PMCID: PMC3110888
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00157.2010
MicroRNAs in skin and wound healing
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small endogenous RNA molecules ∼22 nt in length. miRNAs are capable of posttranscriptional gene regulation by binding to their target messenger RNAs (mRNAs), leading to mRNA degradation or suppression of translation. miRNAs have recently been shown to play pivotal roles in skin development and are linked to various skin pathologies, cancer, and wound healing. This review focuses on the role of miRNAs in cutaneous biology, the various methods of miRNA modulation, and the therapeutic opportunities in treatment of skin diseases and wound healing.
Figures


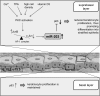
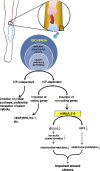


References
-
- Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S, Allgayer H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 27: 2128–2136, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Asano Y. Future treatments in systemic sclerosis. J Dermatol 37: 54–70, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Bagel J. Topical therapies for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. Cutis 84: 3–13, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

