Mammalian Krüppel-like factors in health and diseases
- PMID: 20959618
- PMCID: PMC2975554
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00058.2009
Mammalian Krüppel-like factors in health and diseases
Abstract
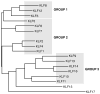
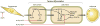
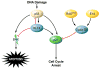
The Krüppel-like factor (KLF) family of transcription factors regulates diverse biological processes that include proliferation, differentiation, growth, development, survival, and responses to external stress. Seventeen mammalian KLFs have been identified, and numerous studies have been published that describe their basic biology and contribution to human diseases. KLF proteins have received much attention because of their involvement in the development and homeostasis of numerous organ systems. KLFs are critical regulators of physiological systems that include the cardiovascular, digestive, respiratory, hematological, and immune systems and are involved in disorders such as obesity, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and inflammatory conditions. Furthermore, KLFs play an important role in reprogramming somatic cells into induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells and maintaining the pluripotent state of embryonic stem cells. As research on KLF proteins progresses, additional KLF functions and associations with disease are likely to be discovered. Here, we review the current knowledge of KLF proteins and describe common attributes of their biochemical and physiological functions and their pathophysiological roles.
Figures


References
-
- Adam PJ, Regan CP, Hautmann MB, Owens GK. Positive- and negative-acting Kruppel-like transcription factors bind a transforming growth factor beta control element required for expression of the smooth muscle cell differentiation marker SM22alpha in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:37798–37806. - PubMed
-
- Adelman CA, Chattopadhyay S, Bieker JJ. The BMP/BMPR/Smad pathway directs expression of the erythroid-specific EKLF and GATA1 transcription factors during embryoid body differentiation in serum-free media. Development. 2002;129:539–549. - PubMed
-
- Agell L, Hernandez S, de Muga S, Lorente JA, Juanpere N, Esgueva R, Serrano S, Gelabert A, Lloreta J. KLF6 and TP53 mutations are a rare event in prostate cancer: distinguishing between Taq polymerase artifacts and true mutations. Mod Pathol. 2008;21:1470–1478. - PubMed
-
- Akaogi K, Nakajima Y, Ito I, Kawasaki S, Oie SH, Murayama A, Kimura K, Yanagisawa J. KLF4 suppresses estrogen-dependent breast cancer growth by inhibiting the transcriptional activity of ERalpha. Oncogene. 2009;28:2894–2902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

