Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in the heart: angels versus demons in a heart-breaking tale
- PMID: 20959622
- PMCID: PMC3808831
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00054.2009
Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in the heart: angels versus demons in a heart-breaking tale
Abstract
Among the myriad of intracellular signaling networks that govern the cardiac development and pathogenesis, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are prominent players that have been the focus of extensive investigations in the past decades. The four best characterized MAPK subfamilies, ERK1/2, JNK, p38, and ERK5, are the targets of pharmacological and genetic manipulations to uncover their roles in cardiac development, function, and diseases. However, information reported in the literature from these efforts has not yet resulted in a clear view about the roles of specific MAPK pathways in heart. Rather, controversies from contradictive results have led to a perception that MAPKs are ambiguous characters in heart with both protective and detrimental effects. The primary object of this review is to provide a comprehensive overview of the current progress, in an effort to highlight the areas where consensus is established verses the ones where controversy remains. MAPKs in cardiac development, cardiac hypertrophy, ischemia/reperfusion injury, and pathological remodeling are the main focuses of this review as these represent the most critical issues for evaluating MAPKs as viable targets of therapeutic development. The studies presented in this review will help to reveal the major challenges in the field and the limitations of current approaches and point to a critical need in future studies to gain better understanding of the fundamental mechanisms of MAPK function and regulation in the heart.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

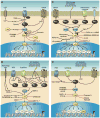

References
-
- Heart disease and stroke statistics: 2008 update. American Heart Association; 2008.
-
- Adjei AA, Cohen RB, Franklin W, Morris C, Wilson D, Molina JR, Hanson LJ, Gore L, Chow L, Leong S, Maloney L, Gordon G, Simmons H, Marlow A, Litwiler K, Brown S, Poch G, Kane K, Haney J, Eckhardt SG. Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharma-codynamic study of the oral, small-molecule mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in patients with advanced cancers. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2139–2146. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akaike M, Che W, Marmarosh N, Ohta S, Osawa M, Ding B, Berk B, Yan C, Abe J. The hinge-helix 1 region of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma 1 (PPARgamma1) mediates interaction with extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 and PPAR-gamma1 transcriptional activation: involvement in flow-induced PPARgamma activation in endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:8691–8704. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aleshin A, Ananthakrishnan R, Li Q, Rosario R, Lu Y, Qu W, Song F, Bakr S, Szabolcs M, D’Agati V, Liu R, Homma S, Schmidt AM, Yan SF, Ramasamy R. RAGE modulates myocardial injury consequent to LAD infarction via impact on JNK and STAT signaling in a murine model. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008;294:H1823–H1832. - PubMed
-
- Andreka P, Zang J, Dougherty C, Slepak TI, Webster KA, Bishopric NH. Cytoprotection by Jun kinase during nitric oxide-induced cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Circ Res. 2001;88:305–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

