Compensatory expression and substrate inducibility of gamma-glutamyl transferase GGT2 isoform in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 20959624
- PMCID: PMC3003821
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erq316
Compensatory expression and substrate inducibility of gamma-glutamyl transferase GGT2 isoform in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
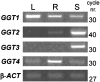
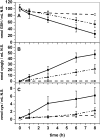
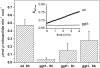
γ-Glutamyl transferases (GGT; EC 2.3.2.2) are glutathione-degrading enzymes that are represented in Arabidopsis thaliana by a small gene family of four members. Two isoforms, GGT1 and GGT2, are apoplastic, sharing broad similarities in their amino acid sequences, but they are differently expressed in the tissues: GGT1 is expressed in roots, leaves, and siliques, while GGT2 was thought to be expressed only in siliques. It is demonstrated here that GGT2 is also expressed in wild-type roots, albeit in very small amounts. GGT2 expression is enhanced in ggt1 knockout mutants, suggesting a compensatory effect to restore GGT activity in the root apoplast. Supplementation with 100 μM glutathione (GSH) resulted in the up-regulation of GGT2 gene expression in wild-type and ggt1 knockout roots, and of GGT1 gene expression in wild-type roots. Glutathione recovery was hampered by the GGT inhibitor serine/borate, suggesting a major role for apoplastic GGTs in this process. These findings can explain the ability of ggt1 knockout mutants to retrieve exogenously added glutathione from the growth medium.
Figures



References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, et al. Genomewide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science. 2003;301:653–657. - PubMed
-
- Beemster G, Fiorani F, Inzé D. Cell cycle: the key to plant growth control? Trends in Plant Science. 2003;8:154–158. - PubMed
-
- Dixon DP, Cummins I, Cole DJ, Edwards R. Glutathione-mediated detoxification systems in plants. Current Opinion in Plant Biology. 1998;1:258–266. - PubMed
-
- Edwards R, Dixon DP, Walbot V. Plant glutathione S-transferases: enzymes with multiple functions in sickness and in health. Trends in Plant Science. 2000;5:193–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

