Epistatic relationships reveal the functional organization of yeast transcription factors
- PMID: 20959818
- PMCID: PMC2990640
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2010.77
Epistatic relationships reveal the functional organization of yeast transcription factors
Abstract
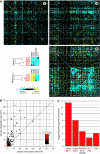
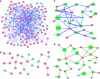
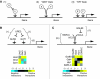
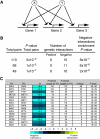
The regulation of gene expression is, in large part, mediated by interplay between the general transcription factors (GTFs) that function to bring about the expression of many genes and site-specific DNA-binding transcription factors (STFs). Here, quantitative genetic profiling using the epistatic miniarray profile (E-MAP) approach allowed us to measure 48 391 pairwise genetic interactions, both negative (aggravating) and positive (alleviating), between and among genes encoding STFs and GTFs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This allowed us to both reconstruct regulatory models for specific subsets of transcription factors and identify global epistatic patterns. Overall, there was a much stronger preference for negative relative to positive genetic interactions among STFs than there was among GTFs. Negative genetic interactions, which often identify factors working in non-essential, redundant pathways, were also enriched for pairs of STFs that co-regulate similar sets of genes. Microarray analysis demonstrated that pairs of STFs that display negative genetic interactions regulate gene expression in an independent rather than coordinated manner. Collectively, these data suggest that parallel/compensating relationships between regulators, rather than linear pathways, often characterize transcriptional circuits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aguilar PS, Frohlich F, Rehman M, Shales M, Ulitsky I, Olivera-Couto A, Braberg H, Shamir R, Walter P, Mann M, Ejsing CS, Krogan NJ, Walther TC (2010) A plasma-membrane E-MAP reveals links of the eisosome with sphingolipid metabolism and endosomal trafficking. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17: 901–908 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Badis G, Chan ET, van Bakel H, Pena-Castillo L, Tillo D, Tsui K, Carlson CD, Gossett AJ, Hasinoff MJ, Warren CL, Gebbia M, Talukder S, Yang A, Mnaimneh S, Terterov D, Coburn D, Yeo AL, Yeo ZX, Clarke ND, Lieb JD et al. (2008) A library of yeast transcription factor motifs reveals a widespread function for Rsc3 in targeting nucleosome exclusion at promoters. Mol Cell 32: 878–887 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

