Feasibility study of two schedules of sunitinib in combination with pemetrexed in patients with advanced solid tumors
- PMID: 20960028
- PMCID: PMC3277823
- DOI: 10.1007/s10637-010-9565-5
Feasibility study of two schedules of sunitinib in combination with pemetrexed in patients with advanced solid tumors
Abstract
Background: Sunitinib is an oral multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors, as well as of other receptor types. We have performed a feasibility study to investigate the safety of sunitinib in combination with pemetrexed for treatment of advanced refractory solid tumors.
Methods: Sunitinib was administered once daily on a continuous daily dosing (CDD) schedule (37.5 mg/day) or a 2-weeks-on, 1-week-off treatment schedule (50 mg/day, Schedule 2/1) in combination with pemetrexed at 500 mg/m(2) on day 1 of repeated 21-day cycles.
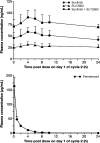
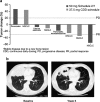
Results: Twelve patients were enrolled in the study: six on the CDD schedule and six on Schedule 2/1. None of the treated patients experienced a dose-limiting toxicity. Toxicities were manageable and similar in type to those observed in monotherapy studies of sunitinib and pemetrexed. Pharmacokinetic analysis did not reveal any substantial drug-drug interaction. One patient with squamous cell lung cancer showed a partial response and five patients had stable disease.
Conclusions: Combination therapy with sunitinib administered on Schedule 2/1 (50 mg/day) or a CDD schedule (37.5 mg/day) together with standard-dose pemetrexed (500 mg/m(2)) was well tolerated in previously treated patients with advanced solid tumors.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00732992.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sunitinib combined with pemetrexed and carboplatin in patients with advanced solid malignancies--results of a phase I dose-escalation study.Invest New Drugs. 2013 Dec;31(6):1487-98. doi: 10.1007/s10637-013-0010-4. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Invest New Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23963796 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I dose-escalation and pharmacokinetic study of sunitinib in combination with pemetrexed in patients with advanced solid malignancies, with an expanded cohort in non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;69(3):709-22. doi: 10.1007/s00280-011-1755-0. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21989766 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sunitinib combined with pemetrexed and cisplatin: results of a phase I dose-escalation and pharmacokinetic study in patients with advanced solid malignancies, with an expanded cohort in non-small cell lung cancer and mesothelioma.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;71(2):307-19. doi: 10.1007/s00280-012-2008-6. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23108697 Clinical Trial.
-
The current status and evolving role of sunitinib in non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2008 Jun;3(6 Suppl 2):S119-23. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318174e9be. J Thorac Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18520293 Review.
-
Alternative dosing schedules for sunitinib as a treatment of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014 Dec;92(3):208-17. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2014.07.006. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014. PMID: 25151214 Review.
Cited by
-
Sunitinib in combination with gemcitabine for advanced solid tumours: a phase I dose-finding study.Br J Cancer. 2013 Apr 16;108(7):1393-401. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.96. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Br J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23511559 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical pharmacokinetics of tyrosine kinase inhibitors: focus on pyrimidines, pyridines and pyrroles.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011 Sep;50(9):551-603. doi: 10.2165/11593320-000000000-00000. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011. PMID: 21827214
-
Sunitinib combined with pemetrexed and carboplatin in patients with advanced solid malignancies--results of a phase I dose-escalation study.Invest New Drugs. 2013 Dec;31(6):1487-98. doi: 10.1007/s10637-013-0010-4. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Invest New Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23963796 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

