Preliminary biochemical characterization of the novel, non-AT1, non-AT2 angiotensin binding site from the rat brain
- PMID: 20960166
- PMCID: PMC3176303
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-010-9328-2
Preliminary biochemical characterization of the novel, non-AT1, non-AT2 angiotensin binding site from the rat brain
Erratum in
- Endocrine. 2010 Oct;38(2):312
Abstract
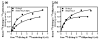
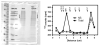
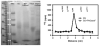
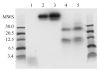
A novel binding site for angiotensins II and III was recently discovered in brain membranes in the presence of the sulfhydryl reactive angiotensinase inhibitor parachloromercuribenzoate. This binding site is distinctly different from the other known receptors for angiotensins: AT₁, AT₂, AT₄, and mas oncogene protein (Ang 1-7 receptor). Preliminary biochemical characterization studies have been done on this protein by crosslinking it with (125)I-labeled photoaffinity probes and solubilizing the radiolabeled binding site. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis studies and isoelectric focusing indicate that this membrane bound binding site is a protein with a molecular weight of 70-85 kDa and an isoelectric point of ~7. Cyanogen bromide hydrolysis of the protein yielded two radiolabeled fragments of 12.5 and 25 kDa. The protein does not appear to be N-glycosylated based upon the failure of PNGaseF to alter its migration rate on a 7.5% polyacrylamide gel. The binding of angiotensin II to this protein is not affected by GTPγS or Gpp(NH)p, suggesting that it is not a G protein-coupled receptor. Further characterization studies are directed to identify this protein either as a novel angiotensin receptor, an angiotensin scavenger (clearance receptor) or an angiotensinase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human brain contains a novel non-AT1, non-AT2 binding site for active angiotensin peptides.Life Sci. 2008 Sep 12;83(11-12):421-5. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2008.07.003. Epub 2008 Jul 22. Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18692076 Free PMC article.
-
Brain angiotensin receptors and binding proteins.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;377(4-6):283-93. doi: 10.1007/s00210-007-0238-7. Epub 2008 Jan 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18172611 Review.
-
Identification of a novel non-AT1, non-AT2 angiotensin binding site in the rat brain.Brain Res. 2007 Apr 27;1143:83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.051. Epub 2007 Jan 24. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17306233
-
Distribution of the non-AT1, non-AT2 angiotensin-binding site in the rat brain: preliminary characterization.Neuroendocrinology. 2008;88(4):256-65. doi: 10.1159/000140635. Epub 2008 Jun 19. Neuroendocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18562784
-
Expression of angiotensin type-1 (AT1) and type-2 (AT2) receptor mRNAs in the adult rat brain: a functional neuroanatomical review.Front Neuroendocrinol. 1997 Oct;18(4):383-439. doi: 10.1006/frne.1997.0155. Front Neuroendocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9344632 Review.
Cited by
-
Renin-Angiotensin System and Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Narrative Review.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Aug 11;7:143. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00143. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 32850989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological characterization of a novel non-AT1, non-AT2 angiotensin binding site identified as neurolysin.Endocrine. 2013 Oct;44(2):525-31. doi: 10.1007/s12020-013-9898-x. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Endocrine. 2013. PMID: 23412923 Free PMC article.
-
LOX-1 and angiotensin receptors, and their interplay.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2011 Oct;25(5):401-17. doi: 10.1007/s10557-011-6331-7. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2011. PMID: 21861069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in the Heart and Lung: Focus on COVID-19.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 20;12:667254. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.667254. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33959029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AT₁ angiotensin II receptor and novel non-AT₁, non-AT₂ angiotensin II/III binding site in brainstem cardiovascular regulatory centers of the spontaneously hypertensive rat.Brain Res. 2010 Nov 4;1359:98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.08.081. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20807518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Severs WB, Summy-Long J, Taylor JS, Connor JD. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1970;174:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Phillips MI. Neuroendocrinology. 1978;25:354–377. - PubMed
-
- Fitzsimons JT. Physiol. Rev. 1998;78:583–686. - PubMed
-
- Osborn JW, Fink GD, Sved AF, Toney GM, Raizada MK. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2007;9:228–235. - PubMed
-
- Phillips MI, Sumners C. Regul. Pept. 1998;78:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

