Parasitic infection reduces dispersal of ciliate host
- PMID: 20961885
- PMCID: PMC3097846
- DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2010.0862
Parasitic infection reduces dispersal of ciliate host
Abstract
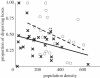
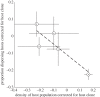
Parasitic infection can modify host mobility and consequently their dispersal capacity. We experimentally investigated this idea using the ciliate Paramecium caudatum and its bacterial parasite Holospora undulata. We compared the short-distance dispersal of infected and uninfected populations in interconnected microcosms. Infection reduced the proportion of hosts dispersing, with levels differing among host clones. Host populations with higher densities showed lower dispersal, possibly owing to social aggregation behaviour. Parasite isolates that depleted host populations most had the lowest impact on host dispersal. Parasite-induced modification of dispersal may have consequences for the spatial distribution of disease, host and parasite genetic population structure, and coevolution.
Figures
References
-
- Thomas F., Guégan J.-F., Renaud F. 2007. Ecology and evolution of parasitism. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press
-
- Bradley C. A., Altizer S. 2005. Parasites hinder monarch butterfly flight: implications for disease spread in migratory hosts. Ecol. Lett. 8, 290–30010.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00722.x (doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00722.x) - DOI - DOI
-
- Cameron P. G., Semlitsch R. D., Bernasconi M. V. 1993. Effects of body size and parasite infection on the locomotory performance of juvenile toads, Bufo bufo. Oikos 66, 129–13610.2307/3545205 (doi:10.2307/3545205) - DOI - DOI
-
- Sorci G., Massot M., Clobert J. 1994. Maternal parasite load increases sprint speed and philopatry in female offspring of the common lizard. Am. Nat. 144, 153–16410.1086/285666 (doi:10.1086/285666) - DOI - DOI
-
- Ronce O. 2007. How does it feel to be like a rolling stone? Ten questions about dispersal evolution. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 38, 231–25310.1146/annurev.ecolsys.38.091206.095611 (doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.38.091206.095611) - DOI - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
