Human pluripotent stem cells produce natural killer cells that mediate anti-HIV-1 activity by utilizing diverse cellular mechanisms
- PMID: 20962093
- PMCID: PMC3014194
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01774-10
Human pluripotent stem cells produce natural killer cells that mediate anti-HIV-1 activity by utilizing diverse cellular mechanisms
Abstract
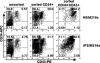
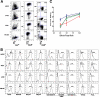
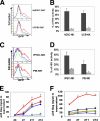
Cell-based therapies against HIV/AIDS have been gaining increased interest. Natural killer (NK) cells are a key component of the innate immune system with the ability to kill diverse tumor cells and virus-infected cells. While NK cells have been shown to play an important role in the control of HIV-1 replication, their functional activities are often compromised in HIV-1-infected individuals. We have previously demonstrated the derivation of NK cells from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) with the ability to potently kill multiple types of tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo. We now demonstrate the derivation of functional NK cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). More importantly, both hESC- and iPSC-derived NK cells are able to inhibit HIV-1 NL4-3 infection of CEM-GFP cells. Additional studies using HIV-1-infected human primary CD4(+) T cells illustrated that hESC- and iPSC-derived NK cells suppress HIV-1 infection by at least three distinct cellular mechanisms: killing of infected targets through direct lysis, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, and production of chemokines and cytokines. Our results establish the potential to utilize hESC- and iPSC-derived NK cells to better understand anti-HIV-1 immunity and provide a novel cellular immunotherapeutic approach to treat HIV/AIDS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of chimeric receptor CD4ζ by natural killer cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells improves in vitro activity but does not enhance suppression of HIV infection in vivo.Stem Cells. 2014 Apr;32(4):1021-31. doi: 10.1002/stem.1611. Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 24307574 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-15-Stimulated Natural Killer Cells Clear HIV-1-Infected Cells following Latency Reversal Ex Vivo.J Virol. 2018 May 29;92(12):e00235-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00235-18. Print 2018 Jun 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29593039 Free PMC article.
-
Lysis of endogenously infected CD4+ T cell blasts by rIL-2 activated autologous natural killer cells from HIV-infected viremic individuals.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Jul 11;4(7):e1000101. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000101. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18617991 Free PMC article.
-
NK Cells in HIV Disease.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2016 Apr;13(2):85-94. doi: 10.1007/s11904-016-0310-3. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2016. PMID: 27002078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fit-For-All iPSC-Derived Cell Therapies and Their Evaluation in Humanized Mice With NK Cell Immunity.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 2;12:662360. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.662360. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33897711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Revolutionizing the treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer: the impact, challenges and strategies of stem cell and genetically engineered cell therapies.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 10;15:1484535. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1484535. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39450176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CAR-cell therapy in the era of solid tumor treatment: current challenges and emerging therapeutic advances.Mol Cancer. 2023 Jan 30;22(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01723-z. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36717905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induced pluripotent stem cells in hematology: current and future applications.Blood Cancer J. 2014 May 9;4(5):e211. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2014.30. Blood Cancer J. 2014. PMID: 24813079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Technology to the Study of Hematological Diseases.Cells. 2017 Mar 8;6(1):7. doi: 10.3390/cells6010007. Cells. 2017. PMID: 28282903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesodermal and hematopoietic differentiation from ES and iPS cells.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2013 Aug;9(4):422-34. doi: 10.1007/s12015-012-9388-1. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2013. PMID: 22684542 Review.
References
-
- Alter, G., M. P. Martin, N. Teigen, W. H. Carr, T. J. Suscovich, A. Schneidewind, H. Streeck, M. Waring, A. Meier, C. Brander, J. D. Lifson, T. M. Allen, M. Carrington, and M. Altfeld. 2007. Differential natural killer cell-mediated inhibition of HIV-1 replication based on distinct KIR/HLA subtypes. J. Exp. Med. 204:3027-3036. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

