Hindbrain noradrenergic A2 neurons: diverse roles in autonomic, endocrine, cognitive, and behavioral functions
- PMID: 20962208
- PMCID: PMC3043801
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00556.2010
Hindbrain noradrenergic A2 neurons: diverse roles in autonomic, endocrine, cognitive, and behavioral functions
Abstract
Central noradrenergic (NA) signaling is broadly implicated in behavioral and physiological processes related to attention, arousal, motivation, learning and memory, and homeostasis. This review focuses on the A2 cell group of NA neurons, located within the hindbrain dorsal vagal complex (DVC). The intra-DVC location of A2 neurons supports their role in vagal sensory-motor reflex arcs and visceral motor outflow. A2 neurons also are reciprocally connected with multiple brain stem, hypothalamic, and limbic forebrain regions. The extra-DVC connections of A2 neurons provide a route through which emotional and cognitive events can modulate visceral motor outflow and also a route through which interoceptive feedback from the body can impact hypothalamic functions as well as emotional and cognitive processing. This review considers some of the hallmark anatomical and chemical features of A2 neurons, followed by presentation of evidence supporting a role for A2 neurons in modulating food intake, affective behavior, behavioral and physiological stress responses, emotional learning, and drug dependence. Increased knowledge about the organization and function of the A2 cell group and the neural circuits in which A2 neurons participate should contribute to a better understanding of how the brain orchestrates adaptive responses to the various threats and opportunities of life and should further reveal the central underpinnings of stress-related physiological and emotional dysregulation.
Figures
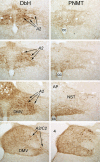
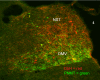
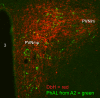

References
-
- Abelson JL, Cameron OG. Adrenergic dysfunction in anxiety disorders. In: Adrenergic Dysfunction and Psychobiology, edited by Cameron OG. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press, 1994
-
- Ahlskog JE, Hoebel BG. Overeating and obesity from damage to a noradrenergic system in the brain. Science 182: 166–169, 1973 - PubMed
-
- Al-Damluji S. Adrenergic mechanisms in the control of corticotropin secretion. J Endocrinol 119: 5–14, 1988 - PubMed
-
- Alonso G, Szafarczyk A, Balmefrezol M, Assenmacher I. Immunocytochemical evidence of stimulatory control by the ventral noradrenergic bundle of parvicellular neurons of the paraventricular nucleus secreting corticotropin-releasing hormone and vasopressin in rats. Brain Res 397: 297–307, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Altschuler SM, Bao X, Bieger D, Hopkins DA, Miselis RR. Viscerotopic representation of the upper alimentary tract in the rat: sensory ganglia and nuclei of the solitary and spinal trigeminal tracts. J Comp Neurol 283: 248–268, 1989 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

