Cutting edge: The adapters EAT-2A and -2B are positive regulators of CD244- and CD84-dependent NK cell functions in the C57BL/6 mouse
- PMID: 20962259
- PMCID: PMC3255554
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001974
Cutting edge: The adapters EAT-2A and -2B are positive regulators of CD244- and CD84-dependent NK cell functions in the C57BL/6 mouse
Abstract
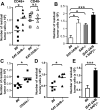
EWS/FLI1-activated transcript 2 (EAT-2)A and EAT-2B are single SH2-domain proteins, which bind to phosphorylated tyrosines of signaling lymphocyte activation molecule family receptors in murine NK cells. While EAT-2 is a positive regulator in human cells, a negative regulatory role was attributed to the adapter in NK cells derived from EAT-2A-deficient 129Sv mice. To evaluate whether the genetic background or the presence of a selection marker in the mutant mice could influence the regulatory mode of these adapters, we generated EAT-2A-, EAT-2B-, and EAT-2A/B-deficient mice using C57BL/6 embryonic stem cells. We found that NK cells from EAT-2A- and EAT-2A/B-deficient mice were unable to kill tumor cells in a CD244- or CD84-dependent manner. Furthermore, EAT-2A/B positively regulate phosphorylation of Vav-1, which is known to be implicated in NK cell killing. Thus, as in humans, the EAT-2 adapters act as positive regulators of signaling lymphocyte activation molecule family receptor-specific NK cell functions in C57BL/6 mice.
Figures
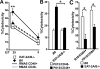


Similar articles
-
The adaptor protein 3BP2 binds human CD244 and links this receptor to Vav signaling, ERK activation, and NK cell killing.J Immunol. 2005 Oct 1;175(7):4226-35. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.7.4226. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16177062
-
Unidirectional signaling triggered through 2B4 (CD244), not CD48, in murine NK cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2010 Oct;88(4):707-14. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0410198. Epub 2010 Jul 20. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20647560
-
Negative regulation of natural killer cell function by EAT-2, a SAP-related adaptor.Nat Immunol. 2005 Oct;6(10):1002-10. doi: 10.1038/ni1242. Epub 2005 Aug 28. Nat Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16127454
-
Of mice and men: different functions of the murine and human 2B4 (CD244) receptor on NK cells.Immunol Lett. 2006 Jun 15;105(2):180-4. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2006.02.006. Epub 2006 Mar 15. Immunol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16621032 Review.
-
Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:197-223. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.197. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11244035 Review.
Cited by
-
Tyrosine kinase Btk is required for NK cell activation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 6;287(28):23769-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.372425. Epub 2012 May 15. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22589540 Free PMC article.
-
2B4 (CD244) induced by selective CD28 blockade functionally regulates allograft-specific CD8+ T cell responses.J Exp Med. 2014 Feb 10;211(2):297-311. doi: 10.1084/jem.20130902. Epub 2014 Feb 3. J Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 24493803 Free PMC article.
-
Tight regulation of memory CD8(+) T cells limits their effectiveness during sustained high viral load.Immunity. 2011 Aug 26;35(2):285-98. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.05.017. Immunity. 2011. PMID: 21856186 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Donor-Reactive CD8+ T Cell Responses by Selective CD28 Blockade Is Independent of Reduced ICOS Expression.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 22;10(6):e0130490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130490. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26098894 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of CD244 Signaling in Immune Cells of the Tumor Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 28;9:2809. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02809. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30546369 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Orange JS, Ballas ZK. Natural killer cells in human health and disease. Clin Immunol. 2006;118:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL. NK cell recognition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005;23:225–274. - PubMed
-
- Long EO. Regulation of immune responses through inhibitory receptors. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999;17:875–904. - PubMed
-
- Colucci F, Di Santo JP, Leibson PJ. Natural killer cell activation in mice and men: different triggers for similar weapons? Nat. Immunol. 2002;3:807–813. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

