Podoplanin associates with CD44 to promote directional cell migration
- PMID: 20962267
- PMCID: PMC3002391
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-06-0489
Podoplanin associates with CD44 to promote directional cell migration
Abstract
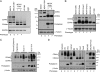
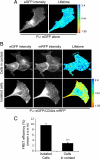
Podoplanin is a transmembrane glycoprotein up-regulated in different human tumors, especially those derived from squamous stratified epithelia (SCCs). Its expression in tumor cells is linked to increased cell migration and invasiveness; however, the mechanisms underlying this process remain poorly understood. Here we report that CD44, the major hyaluronan (HA) receptor, is a novel partner for podoplanin. Expression of the CD44 standard isoform (CD44s) is coordinately up-regulated together with that of podoplanin during progression to highly aggressive SCCs in a mouse skin model of carcinogenesis, and during epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). In carcinoma cells, CD44 and podoplanin colocalize at cell surface protrusions. Moreover, CD44 recruitment promoted by HA-coated beads or cross-linking with a specific CD44 antibody induced corecruitment of podoplanin. Podoplanin-CD44s interaction was demonstrated both by coimmunoprecipitation experiments and, in vivo, by fluorescence resonance energy transfer/fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FRET/FLIM), the later confirming its association on the plasma membrane of cells with a migratory phenotype. Importantly, we also show that podoplanin promotes directional persistence of motility in epithelial cells, a feature that requires CD44, and that both molecules cooperate to promote directional migration in SCC cells. Our results support a role for CD44-podoplanin interaction in driving tumor cell migration during malignancy.
Figures






References
-
- Akhurst R. J., Balmain A. Genetic events and the role of TGF beta in epithelial tumour progression. J. Pathol. 1999;187:82–90. - PubMed
-
- Atsumi N., Ishii G., Kojima M., Sanada M., Fujii S., Ochiai A. Podoplanin, a novel marker of tumor-initiating cells in human squamous cell carcinoma A431. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008;373:36–41. - PubMed
-
- Burns P. A., Kemp C. J., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P., Bremner R., Balmain A. Loss of heterozygosity and mutational alterations of the p53 gene in skin tumours of interspecific hybrid mice. Oncogene. 1991;6:2363–2369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

