An integrated genomic and epigenomic approach predicts therapeutic response to zebularine in human liver cancer
- PMID: 20962331
- PMCID: PMC3077922
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001338
An integrated genomic and epigenomic approach predicts therapeutic response to zebularine in human liver cancer
Abstract
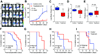
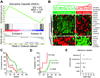
Epigenomic changes such as aberrant hypermethylation and subsequent atypical gene silencing are characteristic features of human cancer. Here, we report a comprehensive characterization of epigenomic modulation caused by zebularine, an effective DNA methylation inhibitor, in human liver cancer. Using transcriptomic and epigenomic profiling, we identified a zebularine response signature that classified liver cancer cell lines into two major subtypes with different drug responses. In drug-sensitive cell lines, zebularine caused inhibition of proliferation coupled with increased apoptosis, whereas drug-resistant cell lines showed up-regulation of oncogenic networks (for example, E2F1, MYC, and TNF) that drive liver cancer growth in vitro and in preclinical mouse models. Assessment of zebularine-based therapy in xenograft mouse models demonstrated potent therapeutic effects against tumors established from zebularine-sensitive but not zebularine-resistant liver cancer cells, leading to increased survival and decreased pulmonary metastasis. Integration of the zebularine gene expression and demethylation response signatures allowed differentiation of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma according to their survival and disease recurrence. This integrated signature identified a subclass of patients within the poor-survivor group that is likely to benefit from therapeutic agents that target the cancer epigenome.
Figures



References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74. - PubMed
-
- Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, Liu J, Wang J, Tak WY, Pan H, Burock K, Zou J, Voliotis D, Guan Z. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:25. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Haussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907. - PubMed
-
- Lee JS, Chu IS, Heo J, Calvisi DF, Sun Z, Roskams T, Durnez A, Demetris AJ, Thorgeirsson SS. Classification and prediction of survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Hepatology. 2004;40:667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

