Pharmacodynamics-mediated drug disposition (PDMDD) and precursor pool lifespan model for single dose of romiplostim in healthy subjects
- PMID: 20963535
- PMCID: PMC2976980
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-010-9234-9
Pharmacodynamics-mediated drug disposition (PDMDD) and precursor pool lifespan model for single dose of romiplostim in healthy subjects
Abstract
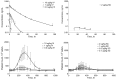
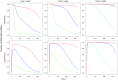
The objective of this study was to characterize the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (PK-PD) of romiplostim after single-dose administration in healthy subjects. The mean serum romiplostim concentrations (PK data) and mean platelet counts (PD data) collected from 32 subjects receiving a single intravenous (0.3, 1 and 10 μg/kg) or subcutaneous (0.1, 0.3, 1, and 2 μg/kg) dose were fitted simultaneously to a mechanistic PK-PD model based on pharmacodynamics-mediated drug disposition (PDMDD) and a precursor pool lifespan concept. The two-compartment PK model incorporated receptor-mediated endocytosis and linear mechanisms as parallel elimination pathways. The maximal concentration of receptors (assumed to be proportional to the platelet count), the equilibrium dissociation constant, and the first-order internalization rate constant for endocytosis of the drug-receptor complex were 0.022 fg/platelet, 0.131 ng/mL, and 0.173 h⁻¹, respectively. Romiplostim concentration stimulates the production of platelet precursors via the Hill function, where the SC₅₀ was 0.052 ng/mL and S (max) was 11.2. The estimated precursor cell and platelet lifespans were 5.9 and 10.5 days, respectively. Model-based simulations revealed that the romiplostim exposure and the platelet response are both dependent on the dose administered and the baseline platelet counts. Also, weekly dosing produced a sustained PD response while dosing intervals ≥2 weeks resulted in fluctuating platelet counts. Thus, the mechanistic PK-PD model was suitable for describing the romiplostim PK-PD interplay (PDMDD), the dose-dependent platelet stimulation, and the lifespans of thrombopoietic cell populations.
Figures







References
-
- Cardier JE, Dempsey J. Thrombopoietin and its receptor, c-mpl, are constitutively expressed by mouse liver endothelial cells: evidence of thrombopoietin as a growth factor for liver endothelial cells. Blood. 1998;91:923–9. - PubMed
-
- Sungaran R, Markovic B, Chong BH. Localization and regulation of thrombopoietin mRNa expression in human kidney, liver, bone marrow, and spleen using in situ hybridization. Blood. 1997;89:101–7. - PubMed
-
- Kuter DJ, Rosenberg RD. The reciprocal relationship of thrombopoietin (c-Mpl ligand) to changes in the platelet mass during busulfan-induced thrombocytopenia in the rabbit. Blood. 1995;85:2720–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

