Tobramycin inhalation powder for P. aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis: the EVOLVE trial
- PMID: 20963831
- PMCID: PMC4112574
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.21356
Tobramycin inhalation powder for P. aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis: the EVOLVE trial
Abstract
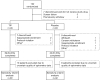
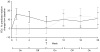
Tobramycin inhalation solution is used to treat chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients. We evaluated the efficacy and safety of a novel, light-porous particle, dry-powder formulation of tobramycin, which was developed to improve delivery efficiency to the airways and substantially reduce the delivery time. In this randomized, double-blind study, patients with CF (age 6-21 years) received tobramycin inhalation powder (112 mg tobramycin) twice daily (n = 46) or placebo (n = 49) via the T-326 Inhaler for one cycle, followed by two open-label cycles (all patients). Cycles were 28 days on, 28 days off treatment. The primary endpoint was change in forced expiratory volume in 1 sec (FEV1) % predicted from baseline to Day 28 of Cycle 1. The study was terminated early based on positive results in the interim analysis. Tobramycin inhalation powder significantly improved FEV1 % predicted versus placebo at Day 28 (difference 13.3, 95% CI: 5.31-21.28; P = 0.0016). Similar changes in FEV1 were seen in patients switching from placebo to tobramycin inhalation powder in Cycle 2; improvements were maintained over time. Tobramycin inhalation powder also reduced sputum P. aeruginosa density, respiratory-related hospitalization and antipseudomonal antibiotic use versus placebo. The most common adverse event was cough; the frequency of cough was higher in patients receiving placebo (26.5%) versus tobramycin inhalation powder (13.0%) in Cycle 1. Tobramycin inhalation powder was not associated with ototoxicity or nephrotoxicity. Administration time was between 4 and 6 min. In conclusion, tobramycin inhalation powder was effective and well tolerated in CF patients, and may offer an important treatment option to decrease the treatment burden of CF pseudomonas lung infections.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; cystic fibrosis; tobramycin inhalation powder.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Gibson RL, Burns JL, Ramsey BW. Pathophysiology and management of pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis. Am J Repir Crit Care Med. 2003;168:918–951. - PubMed
-
- Henry RL, Mellis CM, Petrovic L. Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a marker of poor survival in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1992;12:158–161. - PubMed
-
- Kosorok MR, Zeng L, West SE, Rock MJ, Splaingard ML, Laxova A, Green CG, Collins J, Farrell PM. Acceleration of lung disease in children with cystic fibrosis after Pseudomonas aeruginosa acquisition. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2001;32:277–287. - PubMed
-
- Emerson J, Rosenfeld M, McNamara S, Ramsey B, Gibson RL. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other predictors of mortality and morbidity in young children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2002;34:91–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

